110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

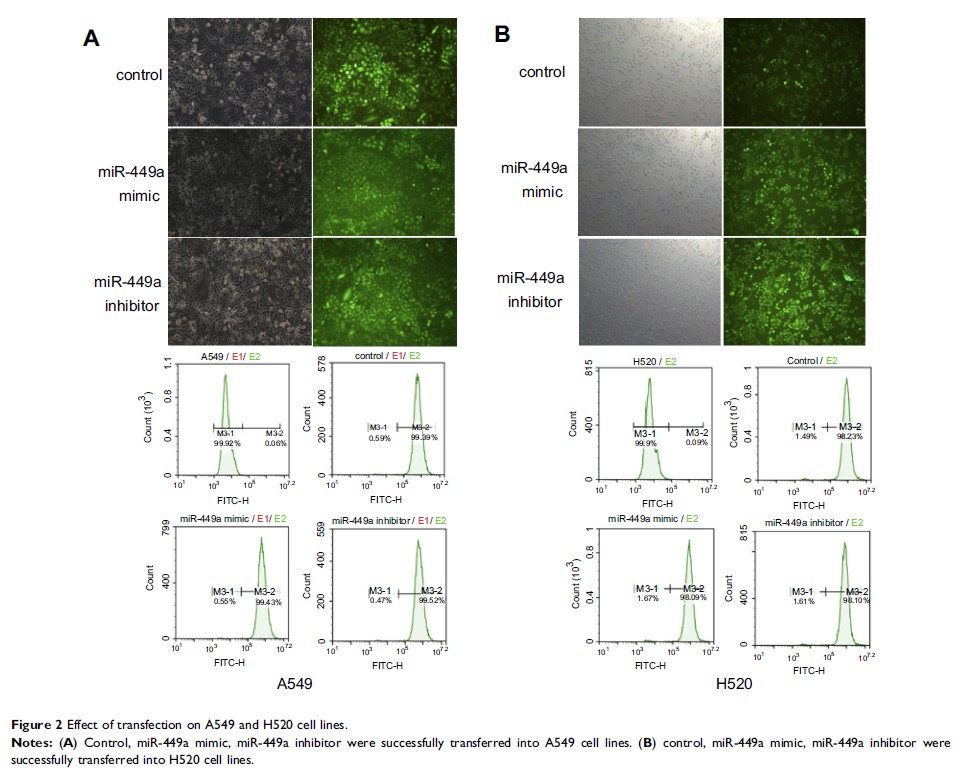
MiR-449a 通过靶向 ADAM10 调节人非小细胞肺癌的细胞迁移和侵袭
Authors Meng H, Huang Q, Zhang X, Huang J, Shen R, Zhang B
Received 9 October 2018
Accepted for publication 25 March 2019
Published 16 May 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 3829—3838
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S190282
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Andrew Yee
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Jianmin Xu
Background: MicroRNAs
(miRNAs) are non-coding small RNAs that have been shown to play a key role in
the development of many tumors. However, its specific mechanism of action in
non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is not very clear.
Purpose: This
study was to identify the effect of miRNA-449a on NSCLC invasion and migration.
Methods: We used
quantitative real-time PCR experiments to demonstrate that miRNA-449a is
down-regulated in NSCLC tissues and cell lines. We also used the Transwell
assay to detect cell invasion and migration, and the Western Blot assay was
used to detect protein expression. The dual luciferase assay was used to detect
the targeting relationship between miR-449a and A Disintegrin And
Metalloproteinases 10 (ADAM10).
Results: Our experiments
demonstrated that miRNA-449a was down-regulated in NSCLC tissues and cell
lines. When miRNA-449a was up-regulated in NSCLC cells, the invasion and
migration ability of the cells was weakened, and the expression of ADAM10 was
decreased. After down-regulation of miRNA-449a, the cell’s invasion and
migration ability was enhanced, and the expression of ADAM10 was increased.
Through dual luciferase assays, we also found that miRNA-449a can target ADAM10
to delay the progression of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and inhibit
invasion and migration.
Conclusion: Our
experiments demonstrated that miRNA-449a acted as a tumor suppressor gene
through inhibiting the expression of ADAM10 in NSCLC.
Keywords: miR-449a,
non-small cell lung cancer, NSCLC, ADAM10, epithelial-mesenchymal transition,
EMT