110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

XPC 多态性对铂类化疗反应的影响:荟萃分析
Authors Xie C, Zhao J, Hua W, Tan P, Chen Y, Rui J, Sun X, Fan J, Wei X, Xu X, Yang X
Received 23 January 2019
Accepted for publication 28 March 2019
Published 16 May 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 3839—3848
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S202617
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Aruna Narula
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Takuya Aoki
Objective: As an
important DNA repair gene, the xeroderma pigmentosum complementation group C
(XPC) gene and its functional genetic variants’ relationship with chemotherapy
response has been extensively studied. To quantitatively elucidate the genetic
impact of the XPC rs2228000 and rs2228001 polymorphisms on the
response to platinum-based chemotherapy, the present meta-analysis was
conducted.
Materials and methods: A
systematic literature search was performed in seven cyber databases until
February 20, 2019, for all relevant studies that assessed the relationship
between XPC polymorphisms
and the response to platinum-based chemotherapy. Odds ratios (ORs) with a 95%
confidence interval (95% CI) were measured to assess the strength of the
association. R programs were developed to perform the statistical analyses,
including calculations of pooled estimates, publication bias and sensitivity
analyses, and heterogeneity interpretations.
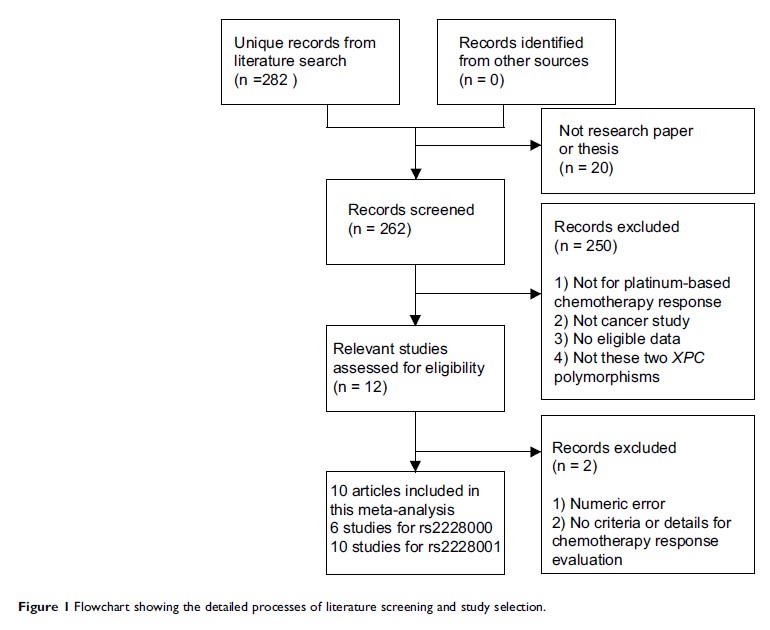
Results: A total
of 1,615 patients from 10 studies for the rs2228001 polymorphism were winnowed
for further statistical analysis. For the rs2228000 polymorphism, 858 samples
from six datasets were included. However, this meta-analysis indicated no
significant effect of these two XPC polymorphisms on the response to
platinum-based chemotherapy. When stratified according to sample size, country
or cancer type, no statistical significance for association was identified in
all subgroups. Further sensitivity analysis and publication bias assessment
ensured the reliability of the meta-analysis.
Conclusions: The
pooled estimates suggest that neither the rs2228000 polymorphism nor the
rs2228001 polymorphism contributes to the genetic predisposition for an altered
response to platinum-based chemotherapy. Considering the limitations of our
present meta-analysis, more studies with large-scale cohorts and rigorous
methods are needed to validate our results.
Keywords: XPC,
polymorphism, meta-analysis, platinum-based chemotherapy