110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

黄芪可改变 2 型糖尿病小鼠的肠道微生物群组成:药理学的线索
Authors Li XY, Shen L, Ji HF
Received 28 January 2019
Accepted for publication 26 March 2019
Published 17 May 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 771—778
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DMSO.S203239
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Justinn Cochran
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Konstantinos Tziomalos
Background: Astragalus possesses
therapeutic effects for type 2 diabetes (T2D), while its action mechanisms
remain to be elucidated. In view of the pathogenic associations between gut
microbiota and T2D, we explored the effect of astragalus on gut-microbiota
composition of T2D mice.
Materials and methods: Modulation effects of astragalus on gut microbiota of
T2D-model mice were assessed by 16S rRNA gene sequencing.
Results: Inhibited blood-glucose and body-weight levels of T2D mice by
astragalus were accompanied by gut microbiota–composition alteration.
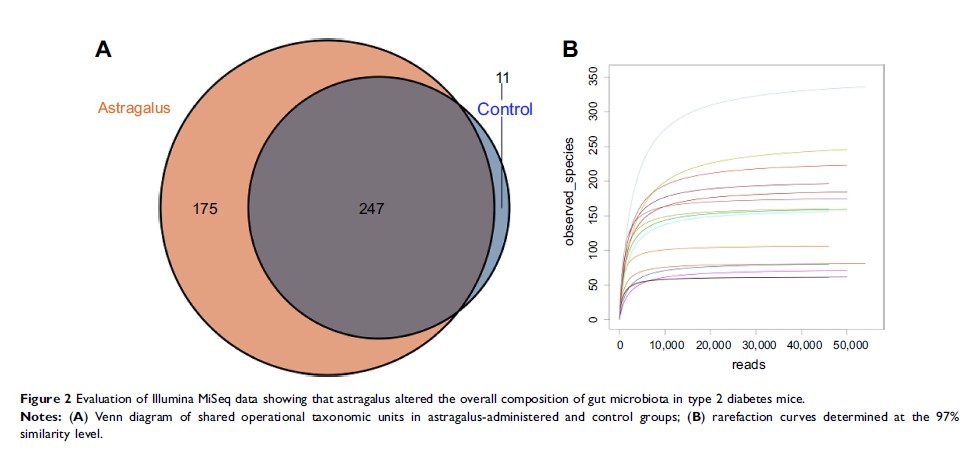
Astragalus administration significantly increased gut-microbiota richness and
diversity in T2D mice and significantly altered the abundance of several
bacterial taxa, inducing increased abundance of Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium .
PICRUSt software revealed the relationship between astragalus and T2D.
Conclusion: Due to previously reported decreased gut-microbiota richness
and diversity and reduced abundance of key species of Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium ,
more studies are encouraged to explore the contribution of gut-microbiota
alteration by astragalus to its anti-T2D effect.
Keywords: astragalus,
type 2 diabetes, gut microbiota, alteration, 16S rRNA gene sequencing