110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

microRNA-605 通过直接靶向 Forkhead Box P1 抑制非小细胞肺癌的致癌性
Authors Zhou W, Li R
Received 6 November 2018
Accepted for publication 4 March 2019
Published 17 May 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 3765—3777
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S193675
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Geoffrey Pietersz
Background and aims: microRNA-605
(miR-605) is dysregulated in multiple cancers and plays crucial roles in
regulating cancer progression. However, little is known about the expression
pattern and detailed roles of miR-605 in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
Thus, in this study, we evaluated miR-605 expression in NSCLC along with its
clinical significance. More importantly, the detailed roles and the underlying
molecular mechanisms of miR-605 in NSCLC were explored.
Material and methods: Quantitative
reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) was employed to
detect miR-605 expression in NSCLC tissues and cell lines. A series of
experiments were performed to determine the effects of miR-605 upregulation on
NSCLC cell proliferation, apoptosis, migration and invasion in vitro and tumor
growth in vivo. In addition, the downstream regulatory mechanisms of miR‐605
action in NSCLC cells were explored.
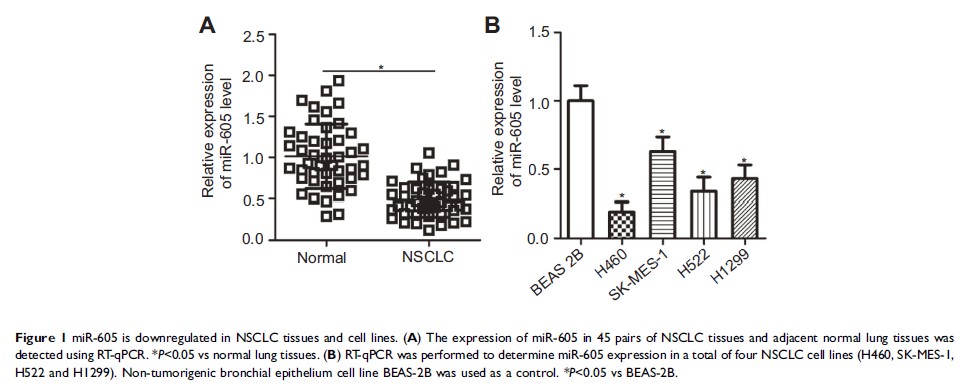
Results: Decreased
expression of miR-605 was frequently detected in NSCLC tissues and cell lines.
Low expression of miR-605 was significantly correlated with the tumor size, TNM
stage, and distane metastasis in NSCLC patients. Exogenous miR-605 expression
inhibited proliferation, increased apoptosis, and inhibited metastasis of NSCLC
cells in vitro. Additionally, miR-605 overexpression hindered the growth of
NSCLC cells in vivo. Furthermore, Forkhead Box P1 (FOXP1) was identified as a
direct target gene of miR-605 in NSCLC cells. Moreover, FOXP1 was highly
expressed in NSCLC cells and showed an inverse correlation with miR-605
expression levels. Besides, silencing of FOXP1 simulated roles similar to
miR-605 upregulation in NSCLC cells. FOXP1 reintroduction partially abolished
the anticancer effects of miR-605 in NSCLC cells.
Conclusion: Our
results revealed that miR-605 inhibited the oncogenicity of NSCLC cells in
vitro and in vivo by directly targeting FOXP1, suggesting the importance of the
miR-605/FOXP1 pathway in the malignant development of NSCLC.
Keywords: non-small-cell
lung cancer, microRNA-605, proliferation, apoptosis, metastasis, Forkhead Box
P1