110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

小儿急性淋巴细胞白血病患者脑脊液的蛋白质组学分析:一项试验研究
Authors Guo L, Ren H, Zeng H, Gong Y, Ma X
Received 29 November 2018
Accepted for publication 4 February 2019
Published 17 May 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 3859—3868
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S193616
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Takuya Aoki
Purpose: Involvement
of central nervous system in acute lymphoblastic leukemia (CNSL) remains one of
the major causes of pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) treatment
failure. However, the current understanding of the pathological process of CNSL
is still limited. This study aimed to better understand the protein expression
in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of ALL and discover valuable prognostic
biomarkers.
Materials and methods: CSF
samples were obtained from ALL patients and healthy controls. Comparative
proteomic profiling using label-free liquid chromatography-tandem mass
spectrometry was performed to detect differentially expressed proteins.
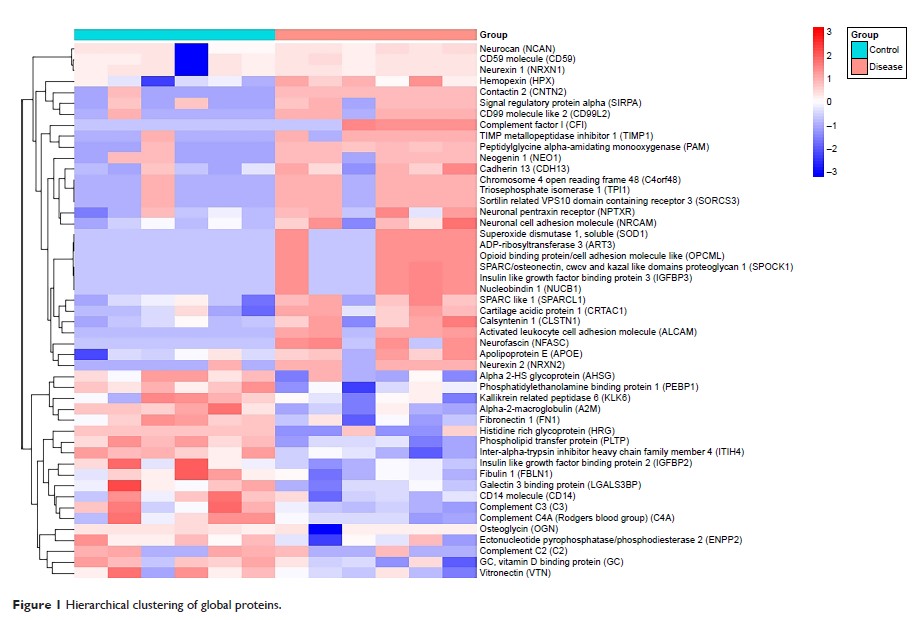
Results: In the
present study, 51 differentially expressed proteins were found. Among them, two
core clusters including ten proteins (TIMP1, LGALS3BP, A2M, FN1, AHSG, HRG,
ITIH4, CF I, C2, and C4a) might be crucial for tumorigenesis and progression of
ALL and can be potentially valuable indicators of CNSL.
Conclusion: These
differentially expressed proteins of ALL children with central nervous system
involvement and normal children may work as diagnostic and prognostic factors
of ALL patients.
Keywords: ALL,
central nervous system leukemia, CSF, mass spectrometry, proteomics