110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

紫杉醇蛋白结合颗粒在乳腺癌患者中的生物等效性:通过快速平衡透析和液相色谱 - 串联质谱法测定血浆中紫杉醇的总量和未结合紫杉醇的数量
Authors Li J, Li W, Dai X, Zhong D, Ding Y, Chen X
Received 7 January 2019
Accepted for publication 23 March 2019
Published 20 May 2019 Volume 2019:13 Pages 1739—1749
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S200679
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Andrew Yee
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Cristiana Tanase
Background and objective: Paclitaxel
protein-bound particles for injectable suspension (nab-paclitaxel) showed many
advantages in safety, effectiveness, and convenience. Different from
conventional formulations, the bioequivalence evaluation of nab-paclitaxel
formulations requires to determine the total amount of paclitaxel in plasma and
the unbound paclitaxel to reflect their in vivo disposition. This study aimed
to develop an analytical method to quantify the total and unbound paclitaxel in
plasma and evaluate the bioequivalence of two formulations of nab-paclitaxel in
patients with breast cancer.
Materials and methods: An
open-label, randomized, two-period crossover study was completed among 24
Chinese patients with breast cancer. The patients were randomized to receive
either the test formulation on cycle 1 day 1 and after 21 days in cycle 2
day 1 by the reference formulation (Abraxane®), or vice versa. Rapid
equilibrium dialysis was adopted to separate the unbound paclitaxel in human
plasma. Total and unbound paclitaxel concentrations were measured by the
validated liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry methods over the range
of 5.00–15,000 and 0.200–200 ng/mL, respectively. The bioequivalence of
the test formulation to the reference formulation was assessed using the Food
and Drug Administration and European Medicines Agency guidelines.
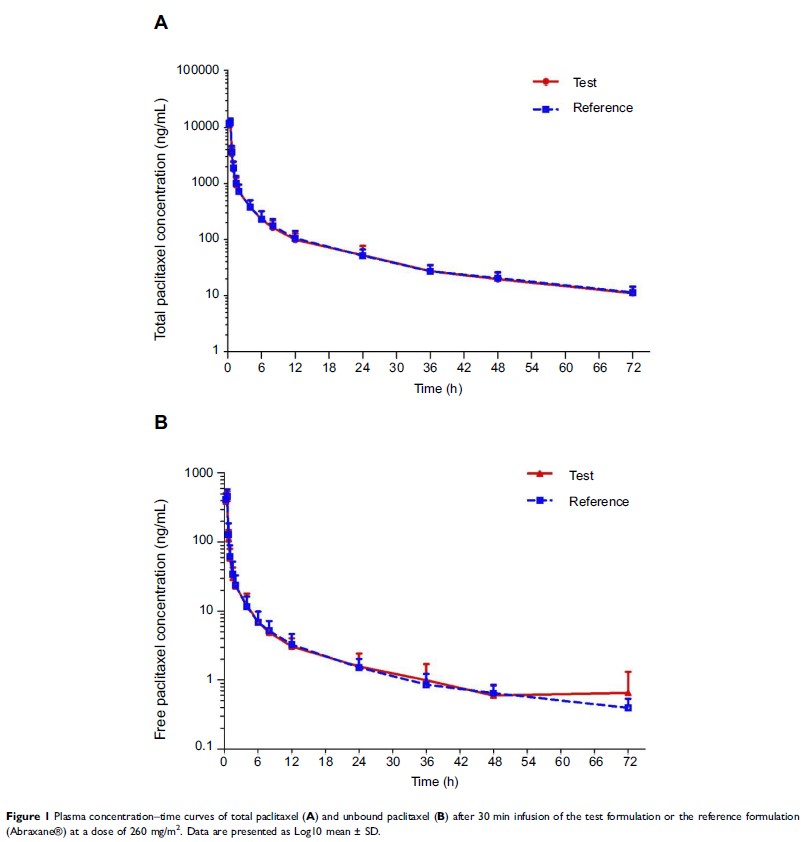
Results: All the
90% confidence intervals (CIs) of the geometric mean ratios fell within the
predetermined acceptance range. The 90% CIs for the area under the
concentration–time curve (AUC) from 0 h to 72 h (AUC0–t), AUC from
time zero to infinity (AUC0–∞), and peak
plasma concentrations (Cmax) for total
paclitaxel were 92.03%–98.05%, 91.98%–99.37%, and 91.37%–99.36%, respectively.
The 90% CIs of AUC0–t, AUC0–∞, and Cmax for
unbound paclitaxel were 86.77%–97.88%, 86.81%–97.88%, and 87.70%–98.86%, respectively.
Conclusion: Bioequivalence
between the two nab-paclitaxel formulations was confirmed for total and unbound
paclitaxel at the studied dose regimen.
Keywords: nab-paclitaxel,
bioequivalence, rapid equilibrium dialysis, unbound fraction, pharmacokinetics