110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

长链非编码 RNA LINC00152 上调可促进食管鳞状细胞癌的增殖和转移
Authors Yang Y, Sun X, Chi C, Liu Y, Lin C, Xie D, Shen X, Lin X
Received 19 December 2018
Accepted for publication 20 April 2019
Published 21 May 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 4643—4654
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S198905
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Nakshatri
Purpose: Esophageal
cancer is a major cause of cancer-related mortality worldwide. The long
noncoding RNA LINC00152 has been confirmed to play an oncogenic role in many
cancers. However, the expression pattern and function of LINC00152 in human
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) remain unclear.
Materials and methods: We
evaluated LINC00152 expression in ESCC by qPCR and in situ hybridization.
Proliferation, apoptosis, cell cycle, migration and invasion were examined in
ESCC cells knocked down for LINC00152 knockdown by siRNA. Furthermore, an mRNA
microarray was performed in ESCC cells with LINC00152 knockdown.
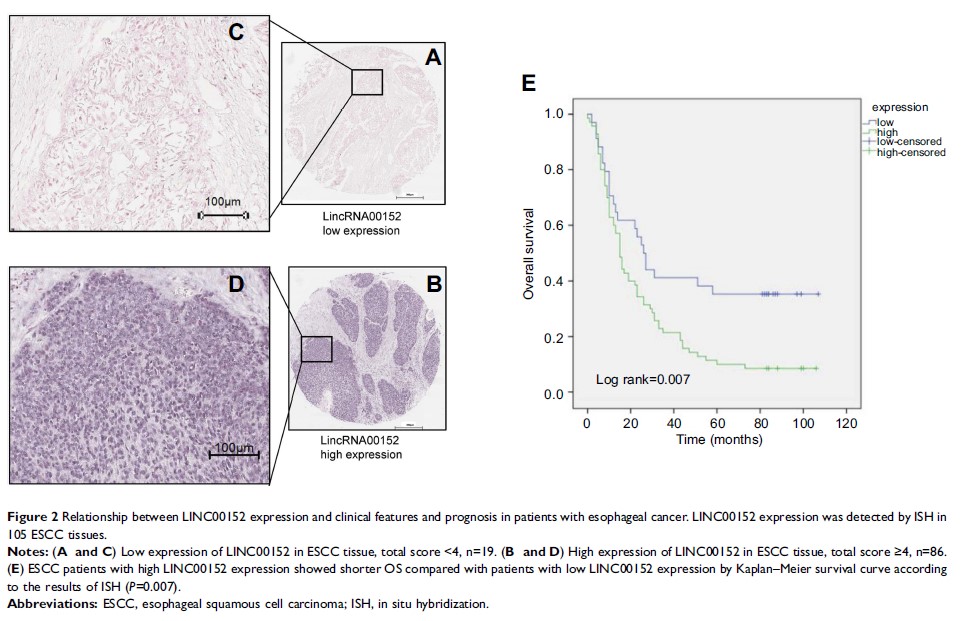
Results: LINC00152
was significantly upregulated in human ESCC clinical samples (P <0.001) and
cell lines (P =0.008),
and LINC00152 overexpression was related to lymphatic metastasis (P =0.03) and
advanced pTNM classification (P =0.005). Furthermore, ESCC patients with LINC00152
overexpression had significantly shorter overall survival (P =0.007), and
LINC00152 overexpression was an independent risk factor for overall survival of
ESCC patients. LINC00152 knockdown inhibited the proliferation, migration and
invasion of ESCC cells in vitro. In addition, mechanistic investigations
through mRNA array and immunoblot analyses demonstrated that LINC00152
regulated the expression of several cell cycle-related proteins and SNARE
(soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor attachment protein receptors)
interactions in vesicular transport pathway proteins.
Conclusion: Our
research indicated that LINC00152 exhibits oncogenic functions in ESCC and may
represent a potential new target for ESCC therapy.
Keywords: LINC00152,
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, proliferation, metastasis