110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

SU5416 通过调节血管内皮细胞的性质减缓脂多糖诱导的小鼠急性肺损伤
Authors Huang X, Zhu J, Jiang Y, Xu C, Lv Q, Yu D, Shi K, Ruan Z, Wang Y
Received 26 September 2018
Accepted for publication 12 March 2019
Published 23 May 2019 Volume 2019:13 Pages 1763—1772
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S188858
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sukesh Voruganti
Background and
aim: A potent and selective vascular
endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR) inhibitor SU5416, has been developed
for the treatment of solid human tumors. The binding of VEGF to VEGFR plays a
crucial role in the pathophysiology of respiratory disorders. However, the
impact of SU5416 on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced acute lung injury (ALI)
remains unclear. Thus, this study aimed to illuminate the biofunction of SU5416
in the mouse model of ALI.
Methods: Wild-type (WT) and toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)-deficient (TLR4−/-) C57BL/6 mice were used to establish LPS-induced ALI model. The primary
pulmonary microvascular endothelial cell (PMVEC) was extracted for detection of
endothelial barrier function.
Results: LPS significantly increased the number of inflammatory cells and
inflammatory cytokines in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF). In addition, LPS
increased alveolar epithelial cells injury, inflammation infiltration and
vascular permeability of PMVEC in WT and TLR4−/- mice. Western blotting experiment indicated VEGF/VEGFR and
TLR4/NF-κB pathways were involved in the progression of LPS-stimulated ALI.
Consistent with previous research, dexamethasone treatment appeared to be an
effective therapeutic for mice with ALI. Moreover, treatment with SU5416
dramatically attenuated LPS-induced immune responses in mice lung tissues via
inhibiting VEGF/VEGFR and TLR4/NF-κB pathways. Finally, SU5416 also decreased
vascular permeability of PMVEC in vitro.
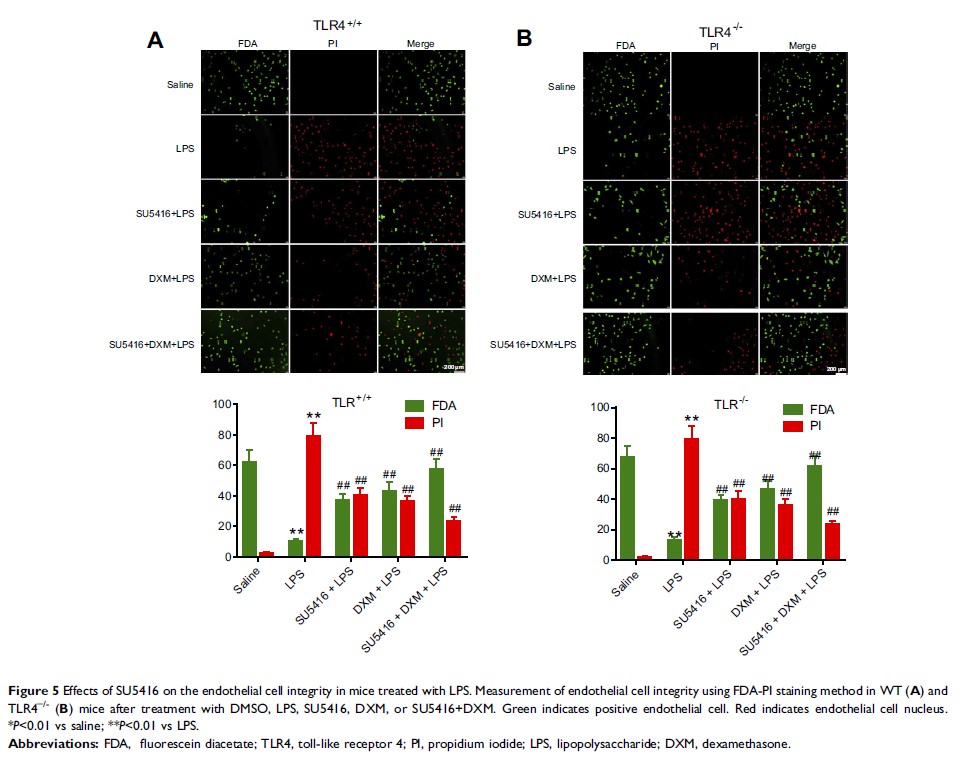
Conclusion: SU5416 ameliorated alveolar epithelial cells injury and
histopathological changes in mice lung via inhibiting VEGF/VEGFR and TLR4/NF-κB
signaling pathways. We also confirmed that SU5416 could restrain vascular
permeability in PMVEC through improving the integrity of endothelial cell.
These findings suggested that SU5416 may serve as a potential agent for the
treatment of patients with ALI.
Keywords: SU5416, lipopolysaccharide, acute lung injury, inflammatory
cytokines