110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

circANKS1B 在结肠直肠癌中发挥 miR-149 的海绵作用以调节 FOXM1 表达并促进细胞迁移和侵袭
Authors Li D, Yang R, Yang L, Wang D, Zhou X, Sun Y
Received 12 January 2019
Accepted for publication 7 March 2019
Published 23 May 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 4065—4073
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S201310
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Aruna Narula
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sanjay Singh
Background: Circular RNAs (circRNAs) and microRNAs (miRNAs) play key roles in
the development of human cancers. CircANKS1B has been reported to be increased
in breast cancer.
Methods: Real-time polymerase chain reaction (real-time PCR) assay was used
to measure expressions of circANKS1B, ANKS1B, and FOXM1. Western blot assay was
employed to examine the protein level of FOXM1 and Slug. The abilities of cell
migration and invasion were measured by wound-healing and transwell assays. The
interaction between circANKS1B and miR-149 was confirmed by site-directed
mutagenesis and luciferase assays.
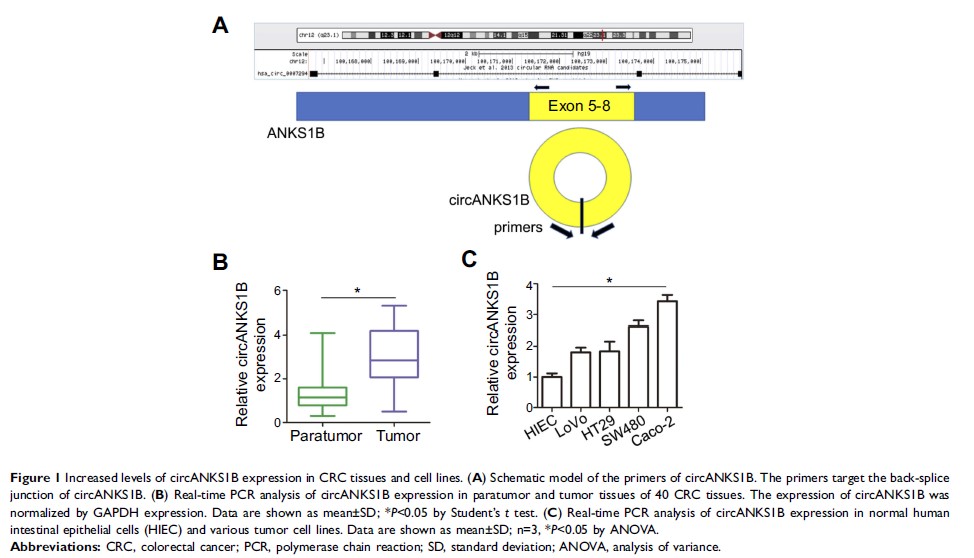
Results: The expression of circANKS1B was up-regulated in colorectal cancer
tissues and cells. Additionally, circANKS1B increased the expression of FOXM1.
Furthermore, the enhancement of CRC cell migration and invasion by circANKS1B
was dependent on FOXM1. However, previous studies have shown that miR-149 can
directly target FOXM1 and act as tumor suppressor in CRC. Consequently, our
results showed that miR-149 could directly bind to circANKS1B and FOXM1. The
inhibition of circANKS1B could reduce FOXM1 and Slug protein levels, thus
suppressing CRC cell migration and invasion.
Conclusion: Taken together, circANKS1B promotes colorectal cancer cell
migration and invasion by acting as a molecular sponge of miR-149 to modulate
FOXM1 and Slug protein levels.
Keywords: circANKS1B, cell invasion, miR-149, FOXM1, colorectal cancer