110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

Calotropin 通过在结直肠癌细胞系中下调 LATS1 激活 YAP
Authors Zhou L, Cai L, Guo Y, Zhang H, Wang P, Yi G, Huang Y
Received 8 January 2019
Accepted for publication 14 April 2019
Published 23 May 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 4047—4054
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S200873
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Rachel Predeepa
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Jianmin Xu
Objectives: Calotropin (CTP), a natural product isolated from Calotropis gigantea , has been identified as a potential
anticancer agent. In this study, we aimed to investigate the effect CTP on
colorectal cancer and the role of Yes-associated protein (YAP) in CTP-inhibited
cell proliferation.
Methods: Cell viability and cell proliferation
were detected by MTT and BrdU assay. Western blotting and immunofluorescence
were performed to determine CTP-induced YAP dephosphorylation and nuclear
localization. Western blotting, siRNA transfection and RT-PCR analysis were
carried out to investigate the mechanisms of CTP-mediated YAP activation. The
anti-tumor activities of CTP were observed in mice tumor models.
Results: We demonstrated that CTP inhibits the
proliferation of colorectal cancer cells both in vitro and in vivo. Moreover,
we showed that CTP activates YAP in colorectal cancer cells. Mechanistically,
CTP promotes LATS1 degradation via the ubiquitination/proteasome pathway,
resulting in YAP dephosphorylation and nuclear localization, leading to induce
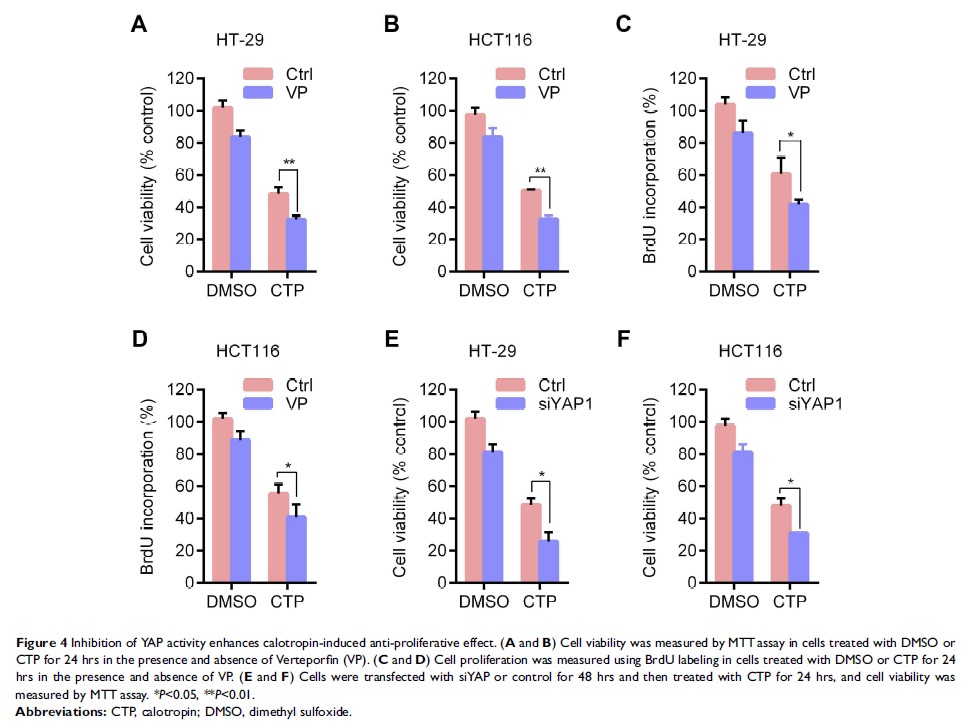
YAP target genes expression in colorectal cancer cells. Inhibition of YAP
activity enhances CTP-mediated inhibition of cell proliferation, suggesting
that YAP plays a protective role in CTP-induced antiproliferative effect.
Conclusion: Our results demonstrate that CTP
markedly inhibits tumor growth and activates a protective role of YAP in
colorectal cancer cells, indicating that combination of CTP and YAP targeting
drugs may be a promising strategy for colorectal cancer treatment.
Keywords: colorectal cancer, calotropin, CTP, cell
proliferation, YAP, LATS1