110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

Eupatilin 通过阻止 G1/S 期细胞周期和破坏细胞骨架结构来抑制胶质瘤的增殖、迁移和侵袭
Authors Fei X, Wang J, Chen C, Ding B, Fu X, Chen W, Wang C, Xu R
Received 8 March 2019
Accepted for publication 30 April 2019
Published 24 May 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 4781—4796
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S207257
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Chien-Feng Li
Purpose: Eupatilin is a pharmacologically active flavonoid extracted from
Asteraceae argyi that has been identified as having antitumor effects. Gliomas
are the most common intracranial malignant tumors and are associated with high
mortality and a poor postoperative prognosis. There are few studies on the
therapeutic effects of eupatilin on glioma. Therefore, we explored the efficacy
and the underlying molecular mechanism of eupatilin on glioma.
Methods: The effect of eupatilin on cell proliferation and viability was
detected using Cell Counting Kit-8 assays. Cell migration was analyzed with a
scratch wound healing assay and invasion was analyzed using transwell assays.
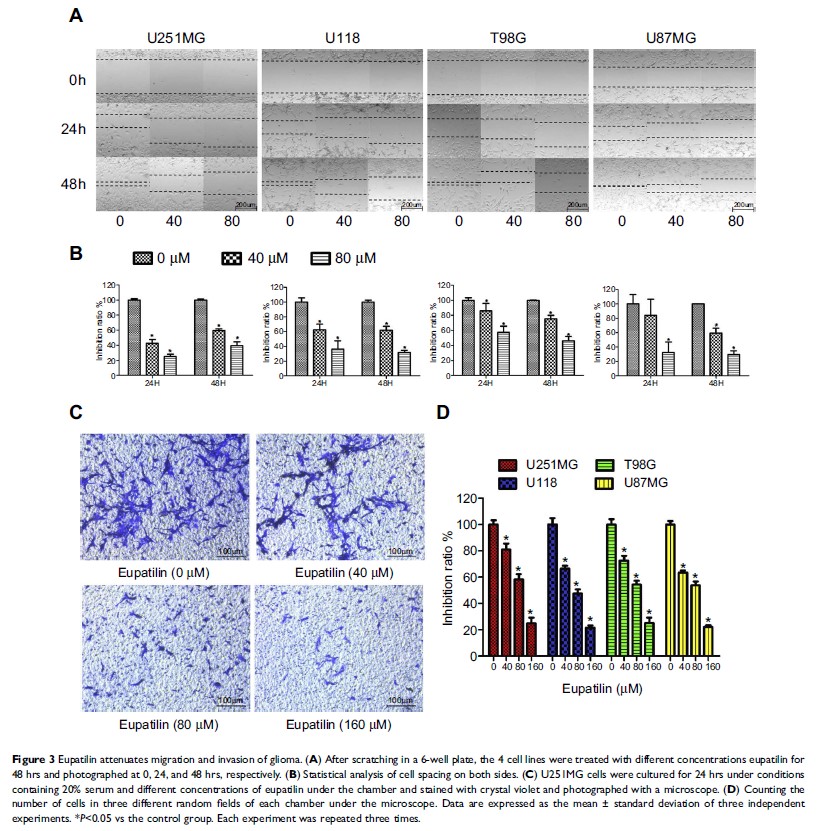
Results: We found that eupatilin significantly inhibits the viability and
proliferation of glioma cells by arresting the cell cycle at the G1/S phase. In
addition, eupatilin disrupts the structure of the cytoskeleton and affects
F-actin depolymerization via the “P-LIMK”/cofilin pathway, thereby inhibiting
the migration of glioma. We also found that eupatilin inhibits the invasion of
gliomas. The underlying mechanism may be related to the destruction of
epithelial–mesenchymal transition, with eupatilin also affecting the
RECK/matrix metalloproteinase pathway. However, we did not observe the
proapoptotic effect of eupatilin on glioma, which is inconsistent with other
studies. Finally, we observed a significant inhibitory effect of eupatilin on
U87MG glioma in xenograft nude mice.
Conclusion: Eupatilin inhibits the viability and proliferation of glioma
cells, attenuates the migration and invasion, and inhibits tumor growth in vivo,
but does not promote apoptosis. Therefore, due to the poor clinical efficacy of
drug treatment of glioma and high drug resistance, the emergence of eupatilin
brings a new dawn for glioma patients.
Keywords: eupatilin, glioma, proliferation, cell cycle, migration, invasion