110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

miR-142-3p 通过靶向 CDC25C、TGFβR1、GNAQ、WASL 和 RAC1 抑制葡萄膜黑色素瘤
Authors Peng D, Dong J, Zhao Y, Peng X, Tang J, Chen X, Wang L, Hu DN, Reinach PS, Qu J, Yan D
Received 22 February 2019
Accepted for publication 18 April 2019
Published 24 May 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 4729—4742
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S206461
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Antonella D'Anneo
Purpose: Uveal melanoma (UM) is the most frequent metastatic ocular tumor
in adults. Therapeutic intervention remains ineffective since none of the novel
procedures used to treat this disease increased survival rates. To deal with
this limitation, additional studies are required to clarify its pathogenesis.
The current study focused on describing how epigenetic modulation by miR-142-3p
affects changes in some cellular functions underlying UM pathogenesis.
Methods and
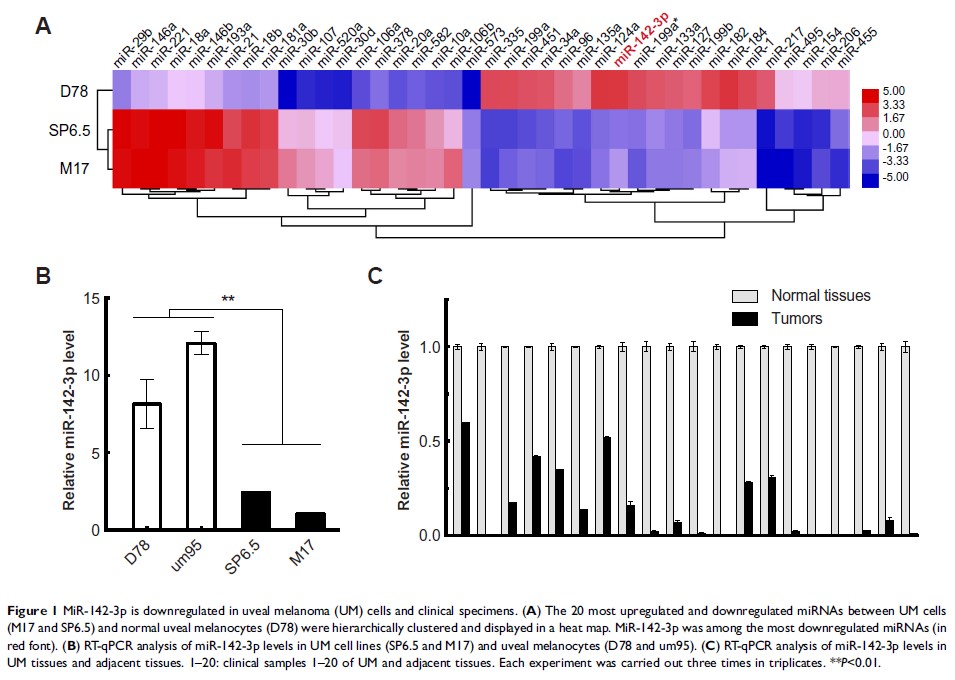
results: Microarray analysis identified 374
miRNAs which were differentially expressed between UM cells and uveal
melanocytes. miR-142-3p was one of the 10 most downregulated miRNAs.
Quantitative RT-PCR analysis confirmed that miR-142-3p expression levels were
significantly decreased in both UM cell lines and clinical specimens. The
results of the MTS, clone formation, scratch wound, transwell assays, and in
vivo biofluorescence imaging showed that miR-142-3p overexpression
significantly inhibited cell proliferation, migration, and invasiveness.
Nevertheless, miR-142-3p did not affect cell apoptotic activity or sensitivity
to doxorubicin. Cell cycle and EdU analysis showed that miR-142-3p
overexpression induced G1/G2 cell cycle arrest and reduced DNA synthesis in UM
cells. Microarray analysis showed that miR-142-3p mainly regulates the TGFβ
signaling pathway, and those in which MAPK and PI3K-Akt are constituents.
Functional interactions between miR-142-3p and CDC25C , TGFβR1 , GNAQ , WASL , and RAC1 target genes were
confirmed based on the results of the luciferase reporter assay and Western
blot analysis. CDC25C or RAC1 downregulation is in agreement with cell cycle
arrest and DNA synthesis disorder induction, while downregulation of TGFβR1,
GNAQ, WASL, or RAC1 accounts for declines in cell migration.
Conclusion: miR-143-3p is a potential therapeutic target to treat UM since
overriding its declines in expression that occur in this disease reversed the
pathogenesis of this disease. Such insight reveals novel biomarker for
decreasing UM vitality and for improved tracking of tumor progression.
Keywords: miR-142-3p, uveal melanoma, tumor suppressor, molecular mechanisms