110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

葡萄籽原花青素 B2 通过调节 PI3K/Aktsignaling 途径促进结直肠癌细胞的自噬和凋亡
Authors Zhang R, Yu Q, Lu W, Shen J, Zhou D, Wang Y, Gao S, Wang Z
Received 22 November 2018
Accepted for publication 7 March 2019
Published 24 May 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 4109—4118
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S195615
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 5
Editor who approved publication: Dr Takuya Aoki
Aim: Colorectal cancer (CRC) is a major malignancy in China, which is
the critical risk of people health. Many natural herbs extracts have been found
to exhibit good therapeutic effect on CRC. Our previous study found that grape
seed procyanidins B2 (PB2) would induce CRC cell death. However, the molecular
mechanism underlying its anti-tumor effect on CRC remains unclear. Thereby,
this study aimed to investigate the anti-tumor mechanism of PB2 on CRC.
Methods: CCK-8, western blotting, flow cytometry, qRT-PCR and animal study
were used in the current study.
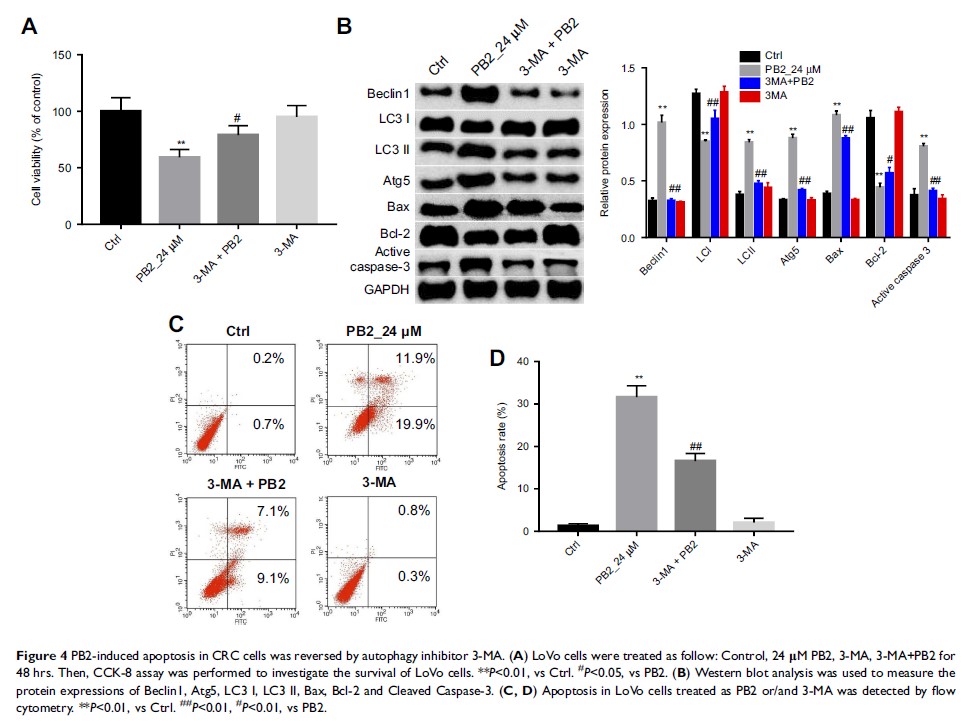
Results: The in vitro and in vivo data demonstrated that PB2 could promote
the apoptosis of CRC cells in a dose-dependent manner, which was significantly
reversed by caspase 3 inhibitor. Meanwhile, PB2 dose-dependently induced
autophagy in CRC cells, which was markedly attenuated by autophagy inhibitor
3-MA. In addition, PB2 dose-dependently inhibited the expressions of p-PI3K,
p-Akt and p-mTOR in the cells.
Conclusion: PB2 dose-dependently induced apoptosis and autophagy in CRC cells
via downregulation of PI3K/Akt pathway. This study provided the experimental
basis for further development of PB2 as a new effective anticancer drug for the
patients with CRC.
Keywords: colorectal cancer, grape seed procyanidin extract, autophagy,
apoptosis, PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway