110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

在前列腺癌的放射治疗中,在直肠内使用肾上腺素
Authors Qin SB, Gao XS, Li HZ, Liu CX, Hou DL, Nian WD, Li XY, Wang D
Received 10 September 2018
Accepted for publication 10 April 2019
Published 27 May 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 4847—4854
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S187049
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 5
Editor who approved publication: Dr Antonella D'Anneo
Purpose: The aim
of the study was to evaluate the feasibility and toxicity of intra-rectal
epinephrine during prostatic radiotherapy.
Materials and methods: A total
of 34 patients with prostate cancer were randomized to receive daily
intra-rectal epinephrine (4 mg in 40 mL, n=16) or placebo (40 mL normal saline,
n=18) 5 min before daily radiotherapy. Physical examination including systolic
blood pressure (SBP) and heart rate (HR) was performed before, 5 min after, and
20 min after intra-rectal use. Toxicities were graded using the Radiation
Therapy Oncology Group standard. A two-sided Fisher’s exact test was used to
compare proportions between groups. A mixed-effects model was used to analyze
multiple measurements of SBP and HR. Survival curves were calculated using the
Kaplan–Meier method and compared between groups using the log-rank test.
Results: All
patients completed the protocol treatment and reported no cardiovascular
symptoms after intra-rectal administration. There were no differences in SBP
and HR between these two groups at any time point (before, 5 min after, and 20
min after epinephrine). At 5 weeks after the start of radiotherapy, the
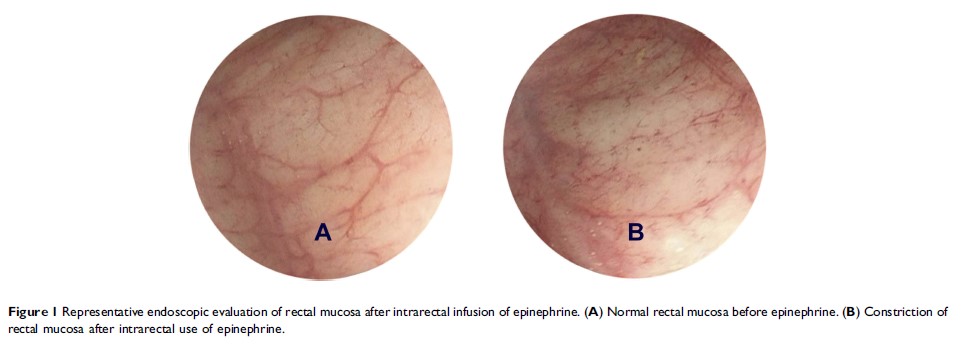
incidence of rectal toxicity≥grade 2 was 27.8% (5/18) for the control group
versus 12.5% (2/16) for the epinephrine group, but was not statistically
significant (p =0.4).
There was no rectal toxicity≥grade 2 in these two groups beyond 2-year
follow-up. The 5-year biochemical relapse-free survival was 75.0% and 72.2% for
the epinephrine and control group, respectively.
Conclusion: Results
of this pilot randomized trial have demonstrated that intra-rectal
administration of epinephrine is feasible and safe in prostatic radiotherapy.
Its radio-protective effect warrants further investigation.
Keywords: radiation
proctitis, epinephrine, radiotherapy