110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

白藜芦醇可通过 P38 丝裂原活化蛋白激酶信号传导下调原代大鼠肺动脉内皮细胞中由 TNF-α 诱导的单核细胞趋化蛋白-1
Authors Lin JW, Yang LH, Ren ZC, Mu DG, Li YQ, Yan JP, Wang LX, Chen C
Received 21 August 2018
Accepted for publication 4 March 2019
Published 27 May 2019 Volume 2019:13 Pages 1843—1853
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S184785
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Arun Kapoor
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Cristiana Tanase
Background: To evaluate the effects of resveratrol to
monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) and the role of p38
mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) in this process in vitro.
Materials and methods: Animal acute pulmonarythromboembolism (PTE) model: rat model was
established by infusion of an autologous blood clot into the pulmonary artery
through a polyethylene catheter. One hundred and thirty-two rats were randomly
and equally divided into ten groups: rats-control (untreated), rats-1% DMSO,
rats-TNF-α, rats-TNF-α + resveratrol, rats-TNF-α +C1142, rats-TNF-α+SB203580,
rats-TNF-α+resveratrol + SB203580, rats-resveratrol only, rats-C1142 only, and
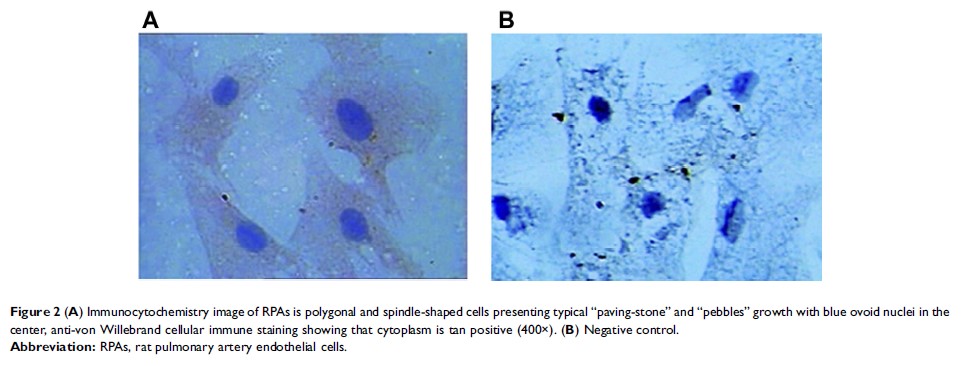
rats-SB203580 only. Rat pulmonary artery endothelial cells (RPAs) tests: RPAs
were isolated from above animal and designated as: RPAs-control, RPAs-1% DMSO
control, RPAs-TNF-α, RPAs-TNF-α + resveratrol, RPAs-TNF-α + C1142, RPAs-TNF-α +
SB203580, RPAs-TNF-α + resveratrol + SB203580, RPAs-resveratrol only,
RPAs-C1142 only, and RPAs-SB203580 only. Each group was further divided into 1,
4, and 8 hrs time point for evaluation (n=6 rats per time point) except
RPAs-TNF-α + SB203580, RPAs-TNF-α + resveratrol + SB203580, RPAs-C1142 and
RPAs-SB203580 only, which were evaluated at 8 hrs time point. At each time
point, mRNA and protein expressions of RPAs of MCP-1 were measured. The
phosphorylation of p38 MAPK (p-pMAPK) of RPAs was also detected.
Results: We
found that the RPAs-TNF-α elicited significant increases in MCP-1 expression
and phosphorylation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (p-p38 MAPK).
Furthermore, the MCP-1 expressions of RPAs-Resveratrol, RPAs-C1142, and
RPAs-SB203580 were significantly down-regulated, which was associated with
robustly suppressed TNF-α-induced p -p38MAPK expression.
Conclusion: Our
findings suggested that MCP-1 was involved in the formation of TNF-α-induced
inflammatory response, and resveratrol could down-regulate the expression of
MCP-1 via TNF-α- inhibition, which might contribute to the decline of acute
PTE-induced PH in vivo.
Keywords: inflammation,
pulmonary artery endothelial cells, pulmonary hypertension, pulmonary
thromboembolism, resveratrol