110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

开发含有硫康唑的纳米乳剂,用于增强透皮吸收和抗真菌活性
Authors Yang Q, Liu S, Gu Y, Tang X, Wang T, Wu J, Liu J
Received 24 February 2019
Accepted for publication 3 May 2019
Published 28 May 2019 Volume 2019:14 Pages 3955—3966
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S206657
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Mian Wang
Background: Sulconazole
(SCZ) is a broad-spectrum transdermally administered anti-fungicidal agent.
However, the therapeutic effect of SCZ is generally limited by its poor water
solubility. This present study aimed to develop and evaluate sulconazole-loaded
nanoemulsions (SCZ-NEs) for enhancement of the transdermal permeation and
antifungal activity.
Methods: A
spontaneous titration method was applied to prepare the SCZ-NEs. And the
optimized formulation of SCZ-NEs was screened by central composite design
(CCD). In addition, the characteristics of the SCZ-NEs were evaluated,
including particle size, zeta potential, drug loading (DL%) and encapsulation
efficiency (EE%). The morphology of SCZ-NEs was observed by transmission
electron microscopy (TEM). Franz diffusion cells were used to evaluate the
transdermal permeability of the SCZ-NEs. The antifungal activity of the SCZ-NEs
was measured by a zone of inhibition (ZOI) test.
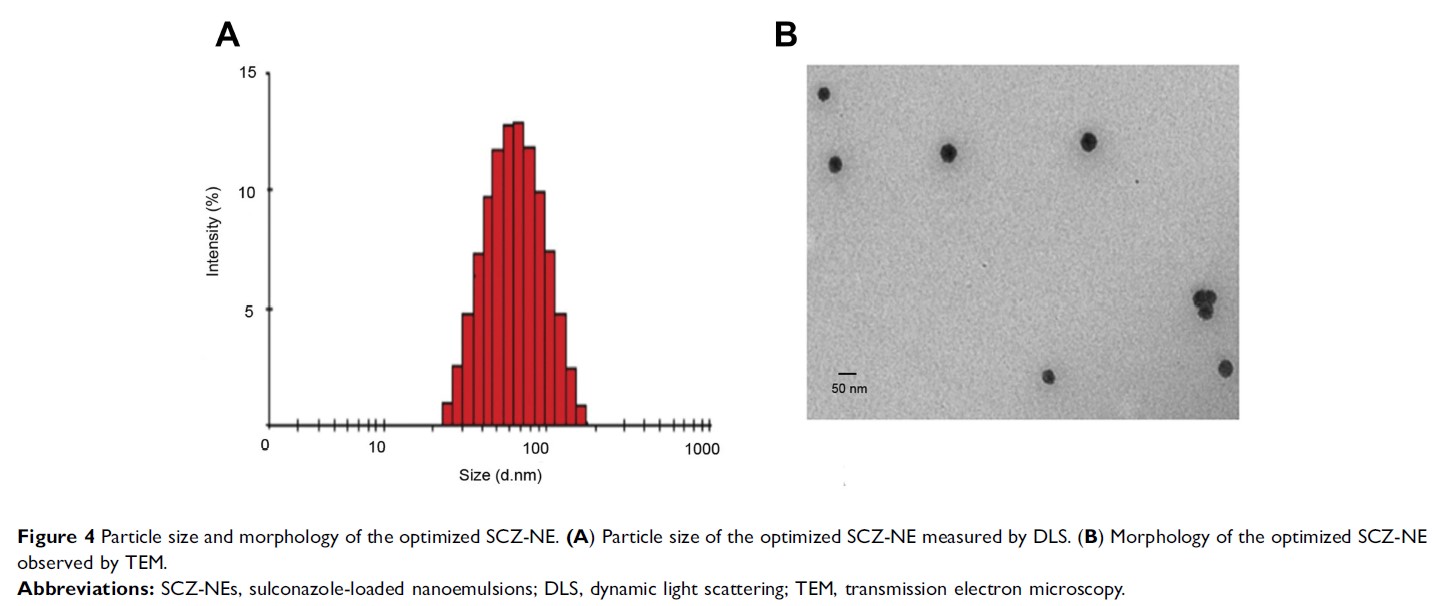
Results: The optimized
SCZ-NEs possessed a moderate particle size of 52.3±3.8 nm, zeta potential of
23.3±1.2 mV, DL% of 0.47±0.05% and EE% of 87.1±3.2%. The ex vivo skin
permeation study verified that the cumulative permeability (Qn) and penetration
rate (Js) of the optimized SCZ-NEs were about 1.7-fold higher than that of a
commercial reference, miconazole (MCZ) cream and 3-fold higher than that of
SCZ-DMSO solution. The optimized SCZ-NEs exhibited zone of inhibition (ZOI)
values of 23.5±2.4 and 20.4±2.5 mm against C. albicans and T. rubrum , which
were larger compared with these of the MCZ cream and SCZ-DMSO solution.
Conclusion: SCZ-NEs
were effectively developed to overcome the poor solubility of SCZ, promote SCZ
permeation through the skin and improve its antifungal activity. Thus, the
SCZ-NEs are a promising percutaneous administration for skin fungal infections
induced by C.
albicans and T. rubrum .
Keywords: sulconazole,
nanoemulsion, central composite design, transdermal delivery, antifungal
activity