110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

胃癌患者接受全腹腔镜下胃癌根治术后早期经口进食的安全性(SOFTLY-1):一项单中心随机对照试验
Authors Wang Q, Yang KL, Guo BY, Shang LF, Yan ZD, Yu J, Zhang D, Ji G
Received 31 December 2018
Accepted for publication 25 March 2019
Published 29 May 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 4839—4846
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S199552
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Antonella D'Anneo
Objectives: The aim of this study is to explore the safety and feasibility of early oral feeding (EOF) on short-term postoperative outcomes.
Trial design: A prospective randomized non-inferiority trial.
Materials and methods: From August 27, 2015 to March 31, 2017, 100 consecutive patients with gastric cancer in Xijing Hospital were recruited. Patients undergoing total laparoscopic radical gastrectomy (TLRG) received either EOF group or delayed oral feeding (DOF group). The endpoints were anastomotic leakage, the recovery of bowel function, the postoperative complications and costs. The process of randomization used a computer-generated sequence that was kept in a sealed envelope by a nurse that did not participate in the trial. None of the participants, administrators of interventions and those assessing outcomes was blinded.
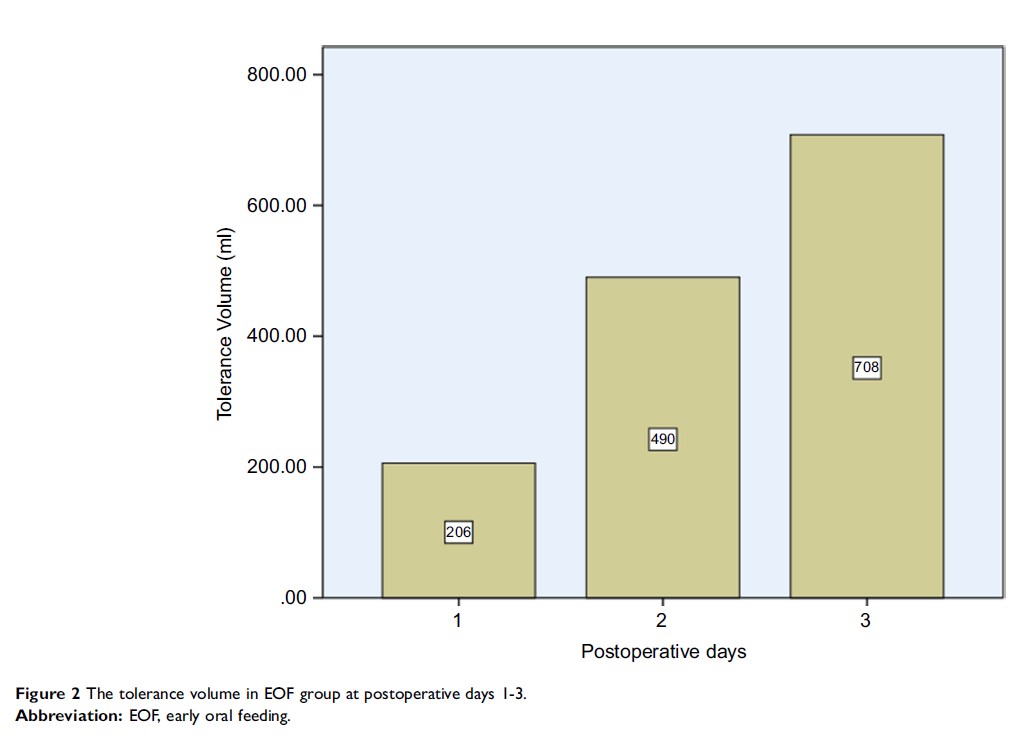
Results: Ultimately, 51 patients were in EOF group and 49 in DOF group, which both are comparable. The postoperative hospital stay in EOF group was significantly lower than DOF group (5.18±1.47 days vs 6.18±2.46 days, P =0.016). Furthermore, there was a trend for a reduction in the time of first flatus (10.3 hrs) and defecation (12.7 hrs) in EOF group compared to DOF group, but it was not statistically significant. Meanwhile, there were no significant differences in postoperative complications between two groups. One patient in the EOF group developed a fistula in the surgical remnant, which was recorded as other leakages; there was no difference between the two groups (P =0.582).
Conclusion: EOF does not seem to be more harmful than DOF, and might significantly improve the short-term outcomes for patients receiving TLRG.
Keywords: gastric cancer, laparoscopic gastrectomy, early oral feeding, postoperative fistula, anastomotic leakage, enhanced recovery after surgery, ERAS