110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

血清乙型肝炎病毒(HBV)DNA 是慢性 HBV 感染的非小细胞肺癌患者生存率的预测生物标志物
Authors Fu Y, Yang X, Liang H, Wu X
Received 18 December 2018
Accepted for publication 26 February 2019
Published 31 May 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 5091—5100
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S198714
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Justinn Cochran
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Professor Nakshatri
Purpose: To study the association between pretreatment serum hepatitis B viral (HBV) DNA copy numbers and clinical outcome of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients with chronic HBV infection.
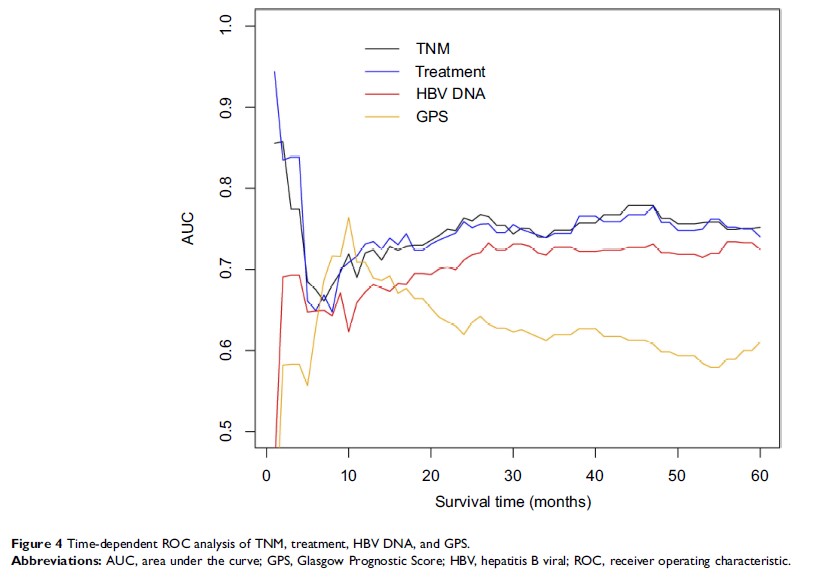
Patients and methods: We retrospectively evaluated the medical records of NSCLC HBV (+) patients between January 2008 and December 2010. The HBV DNA copy numbers and other prognostic factors including albumin (ALB), C-reactive protein (CRP), platelet, neutrophil–lymphocyte ratio (NLR), platelet–lymphocyte ratio (PLR), and Glasgow Prognostic Score (GPS) were obtained before any antitumor treatment. Kaplan–Meier curves and the log-rank test were used to calculate prognostic significance. A multivariable Cox proportional hazard regression was modeled to analyze the independent prognostic factors for NSCLC HBV (+) patients. All independent prognostic factors in the Cox multivariable analysis were used to build a nomogram. The predictive accuracy of HBV DNA, TNM stage and nomogram was evaluated with the concordance index (C-index) and time-dependent receiver operating characteristics (ROC) curves, and simultaneously compared with traditional TNM staging system respectively.
Results: A total of 188 patients were recruited in this study; the median age was 56 years, and the median overall survival (OS) was 34 months. Cox multivariate analysis results showed independent factors for OS including TNM stage (P =0.028), treatment (P =0.002), HBV DNA (P <0.001), and GPS (P =0.026). The nomogram model for survival was built based on four prognostic factors. The C-index for HBV DNA was 0.67, 0.69 for TNM stage, and 0.76 for the nomogram model. There was no statistical difference between HBV DNA and TNM stage (P =0.48). However, the C-index values of nomogram model were statistically higher both than HBV DNA (0.76 vs 0.67, P <0.001), and TNM stage (0.76 vs 0.69, P <0.001).
Conclusion: Pretreatment serum HBV DNA copy numbers can act as a prognostic marker of survival for NSCLC patients with chronic HBV infection.
Keywords: non-small cell lung cancer, hepatitis B, hepatitis B viral DNA, HBV DNA, nomogram, prognosis