110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

小窝蛋白-1(caveolin-1)表达与肝细胞癌的关系:汇总分析和文献回顾
Authors Zhang Y, Fan W, Wu J, Dong J, Cui Z
Received 9 November 2018
Accepted for publication 7 March 2019
Published 31 May 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 5113—5122
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S194033
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Andrew Yee
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Kenan Onel
Background: Aberrant expression of caveolin-1 (CAV-1) is involved in the pathogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC); however, the results have been inconsistent due to the small size of sample in the individual study.
Methods: We performed a meta-analysis and evaluated the association of CAV-1 protein overexpression and clinicopathological significance by using Review Manager 5.2. Pooled ORs and HR with corresponding CIs were calculated.
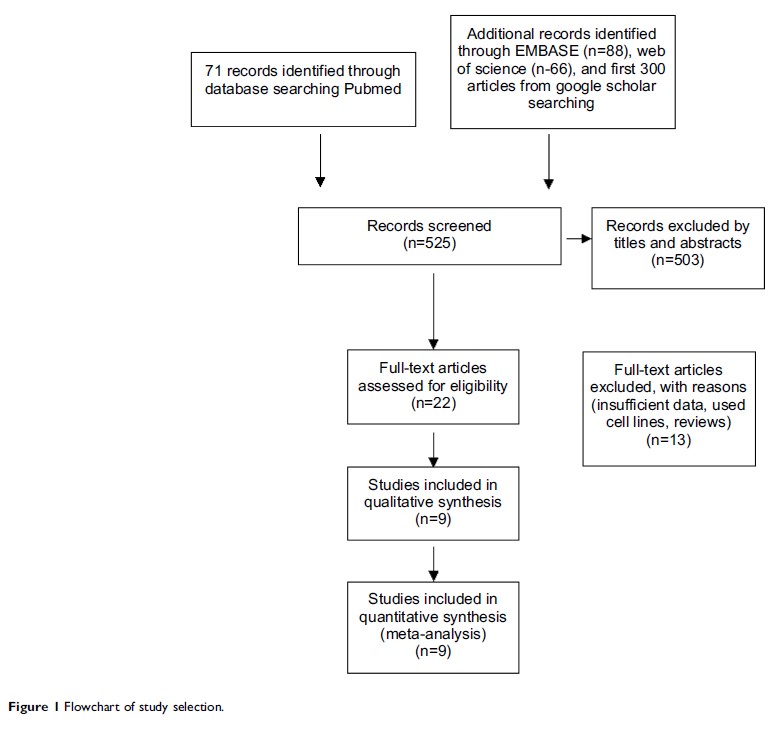
Results: Nine studies were included in the meta-analysis with 810 HCC and 172 cirrhosis patients. CAV-1 protein overexpression was correlated with the risk of cirrhosis; OR was 3.25, p =0.01. Furthermore, the rate of CAV-1 protein overexpression was significantly higher in HCC with cirrhosis than HCC without cirrhosis, suggesting that the CAV-1 protein overexpression likely initiated carcinogenesis in liver with cirrhosis and subsequently contributed to the progression of HCC. In addition, CAV-1 protein overexpression was strongly associated with poor differentiated HCC and invasion; ORs were 2.61 and 2.71, respectively. CAV-1 protein overexpression was strongly correlated with poor overall survival in patients with HCC; HR was 0.4, p =0.03.
Conclusions: In summary, CAV-1 protein overexpression is at risk for liver cirrhosis and HCC derived from cirrhosis, and CAV-1 is also a promising prognostic predictor in HCC.
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma, caveolin-1, prognosis, diagnosis, overexpression