110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

丹酚酸 A 通过调节 PI3K/AKT/mTOR,Bcl-2/Bax/Bax 和胱天蛋白酶-3/分裂的胱天蛋白酶-3 信号通路减弱 CCl4 诱导的肝纤维化
Authors Wang R, Song F, Li S, Wu B, Gu Y, Yuan Y
Received 15 November 2018
Accepted for publication 8 April 2019
Published 31 May 2019 Volume 2019:13 Pages 1889—1900
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S194787
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Cristiana Tanase
Background: Liver fibrosis occurs due to chronic liver disease due to multiple pathophysiological causes. The main causes for this condition are chronic alcohol abuse, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, and infection due to hepatitis C virus. Currently, there is more and more information available about the molecular as well as cellular mechanisms, which play a role in the advancement of liver fibrosis. However, there is still no effective therapy against it.
Purpose: In order to find an effective treatment against liver fibrosis, our study explored whether salvianolic acid A (SA-A), a traditional Chinese medicine extracted from the plant Danshen, could effectively inhibit the liver fibrosis, which is induced by CCl4 in vivo.
Methods: The effects of SA-A were evaluated by assessing the parameters related to liver fibrosis such as body weight, histological changes, and biochemical parameters. Thereafter, the related protein or gene levels of P13K/AKT/mTOR, Bcl-2/Bax and caspase-3/cleaved caspase-3 signaling pathways were determined by western blotting, real-time PCR or immunohistochemistry staining.
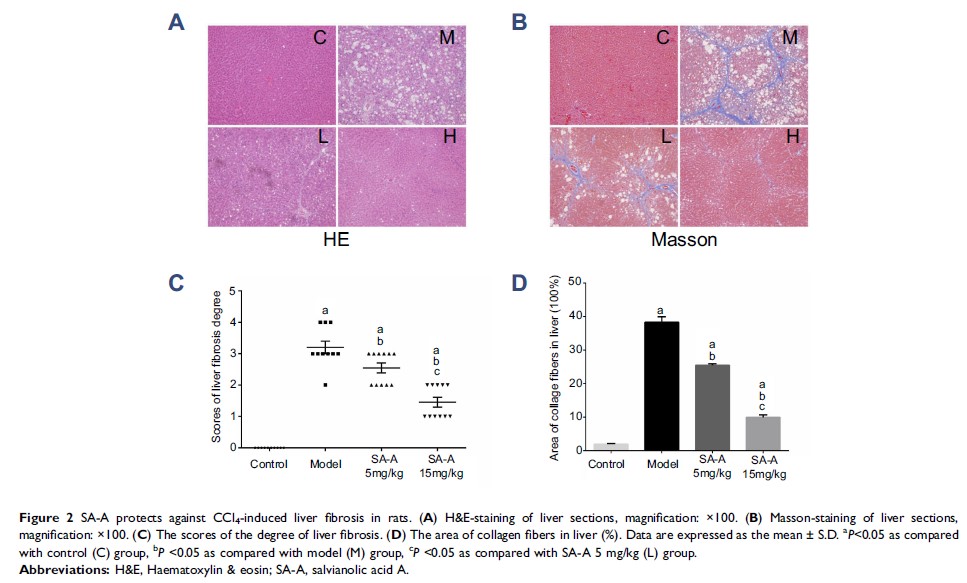
Results: According to the results of our study, SA-A could reduce liver fibrosis by inhibiting liver function, liver fibrosis index, collagen deposition, and improving the degree of liver fibrosis in rats. Mechanistically, the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling cascade was inhibited by SA-A to prevent the stimulation of hepatic stellate cell, as well as the synthesis of extracellular matrix, and regulated Bcl-2/Bax and caspase-3/cleaved caspase-3 signaling pathways to prevent hepatocyte apoptosis.
Conclusion: The novel findings of this study suggested that SA-A could reduce liver fibrosis and the molecular mechanisms behind it are closely associated with the regulation of PI3K/AKT/mTOR, Bcl-2/Bax and caspase-3/cleaved caspase-3 signaling pathways.
Keywords: liver fibrosis, salvianolic acid A, AKT/mTOR, Bcl-2/Bax, caspase-3/cleaved caspase-3