110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

环氧合酶-2 的敲除可使肝细胞癌细胞生长得到抑制并导致细胞周期停滞
Authors Lv X, Chen Z, Li S, Xie H
Received 3 December 2018
Accepted for publication 21 February 2019
Published 31 May 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 4341—4349
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S196822
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Justinn Cochran
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr William Cho
Background & aims: Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) is proved to play important roles in the development and progression of various human tumors, including hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). However, the antitumor effect of RNA interference (RNAi) technology targeting COX-2 in HCC has not yet been verified.
Methods: We silenced COX-2 expression using a lentivirus-mediated RNAi and further investigated the effects of COX-2 knockdown on cell growth and cell cycle in Huh7 and SMMC-7721 cells. COX-2 mRNA was detected by RT-PCR while COX-2 protein was detected by Western blotting. The cell proliferation was measured by MTT assay. The cell cycle was measured by flow cytometry. The tumorigenicity of HCC cells was evaluated using soft-agar clonogenic assay in vitro and nude mouse xenograft model in vivo.
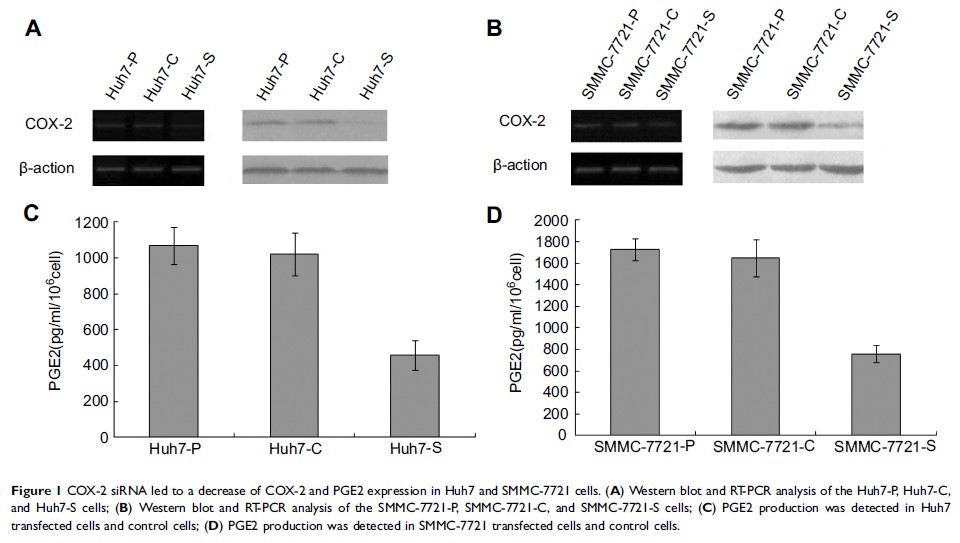
Results: The down-regulation of COX-2 expression significantly inhibited cell proliferation and colony formation, and led to cell cycle arrest in vitro, and reduced the potential of tumorigenicity in vivo in both Huh7 and SMMC-7721 cells. Furthermore, PGE2 production was also decreased after COX-2 expression was suppressed. Finally, knockdown of COX-2 also induced the down-regulation of cell cycle-related protein, cyclinD1.
Conclusions: The abrogation of COX-2 expression can lead to potent antitumor activity and knockdown of COX-2 may be served as a prospective therapeutic strategy against HCC.
Keywords: COX-2, RNA interference, hepatocellular carcinoma