110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

去铁胺诱导的 TfR1 和 DMT1 高表达通过激活 IL-6/PI3K/AKT 通路增强三阴性乳腺癌细胞的铁摄取
Authors Chen C, Liu P, Duan X, Cheng M, Xu LX
Received 5 November 2018
Accepted for publication 19 February 2019
Published 31 May 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 4359—4377
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S193507
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sanjay Singh
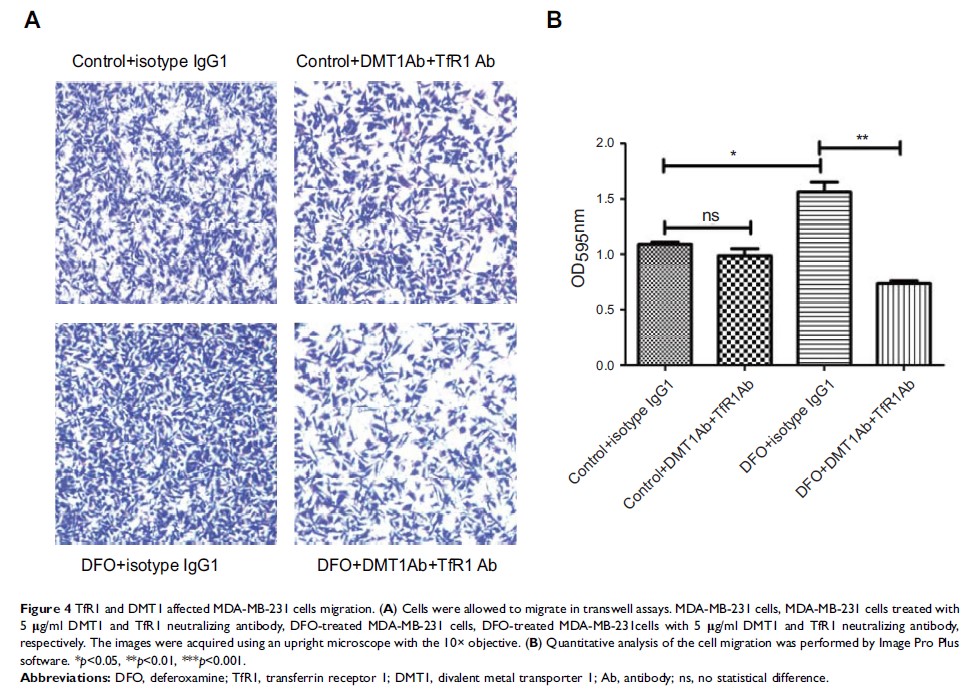
Background: Deferoxamine (DFO) is a commonly used iron chelator, which can reduce the iron levels in cells. DFO is normally used to treat iron-overload disease, including some types of cancer. However, our previous studies revealed that DFO treatment significantly increased the iron concentrations in triple-negative breast cancer cells (TNBCs) resulting in enhanced cell migration. But the mechanism of DFO-induced increasing iron uptake in aggressive TNBCs still remained unclear.
Materials and methods: Iron metabolism-related proteins in aggressive breast cancer MDA-MB-231, HS578T and BT549 cells and nonaggressive breast cancer MCF-7 and T47D cells were examined by immunofluorescence and Western blotting. The possible regulatory mechanism was explored by Western blotting, co-incubation with neutralizing antibodies or inhibitors, and transwell assay.
Results: In this study, we found that DFO treatment significantly increased the levels of iron uptake proteins, DMT1 and TfR1, in aggressive TNBCs. Moreover, both TfR1 and DMT1 expressed on cell membrane were involved in high iron uptake in TNBCs under DFO-induced iron deficient condition. For the possible regulatory mechanism, we found that DFO treatment could promote a high expression level of IL-6 in aggressive MDA-MB-231 cells. The activated IL-6/PI3K/AKT pathway upregulated the expression of iron-uptake related proteins, TfR1 and DMT1, leading to increased iron uptakes.
Conclusion: We demonstrated that DFO could upregulate expression of TfR1 and DMT1 , which enhanced iron uptake via activating IL-6/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in aggressive TNBCs.
Keywords: deferoxamine, iron uptake, TfR1, DMT1