110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

Cholate 修饰的聚合物 - 脂质杂化纳米粒子用于口服递送槲皮素以增强抗白血病效应
Authors Yin J, Hou Y, Song X, Wang P, Li Y
Received 26 March 2019
Accepted for publication 8 May 2019
Published 31 May 2019 Volume 2019:14 Pages 4045—4057
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S210057
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Thiruganesh Ramasamy
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Mian Wang
Background: Quercetin (QUE) shows a potential antileukemic activity, but possesses poor solubility and low bioavailability.
Purpose: This article explored the bile salt transport pathway for oral deliver of QUE using cholate-modified polymer-lipid hybrid nanoparticles (cPLNs) aiming to enhance its antileukemic effect.
Methods: QUE-loaded cPLNs (QUE-cPLNs) were developed through a nanoprecipitation technique and characterized by particle size, entrapment efficiency (EE), microscopic morphology and in vitro drug release. In vitro cellular uptake and cytotoxicity of QUE-cPLNs were examined on Caco-2 and P388 cells; in vivo pharmacokinetics and antileukemic effect were evaluated using Sprague Dawley rats and leukemic model mice, respectively.
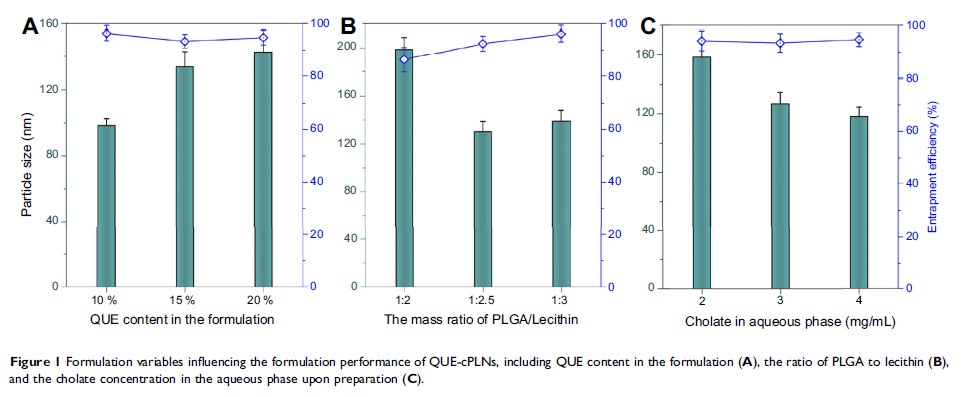
Results: The prepared QUE-cPLNs possessed a particle size of 110 nm around with an EE of 96.22%. QUE-cPLNs resulted in significantly enhanced bioavailability of QUE, up to 375.12% relative to the formulation of suspensions. In addition, QUE-cPLNs exhibited excellent cellular uptake and internalization capability compared to cholate-free QUE-PLNs. The in vitro cytotoxic and in vivo antileukemic effects of QUE-cPLNs were also signally superior to free QUE and QUE-PLNs.
Conclusion: These findings indicate that cPLNs are a promising nanocarrier able to improve the oral bioavailability and therapeutic index of QUE.
Keywords: quercetin, polymer-lipid hybrid nanoparticles, bile salt, bioavailability, leukemia