110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

偶发分枝杆菌引起的白内障后眼内炎对视觉的影响
Authors Di Y, Chen X
Received 14 January 2019
Accepted for publication 29 April 2019
Published 4 June 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 1433—1438
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IDR.S201460
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Joachim Wink
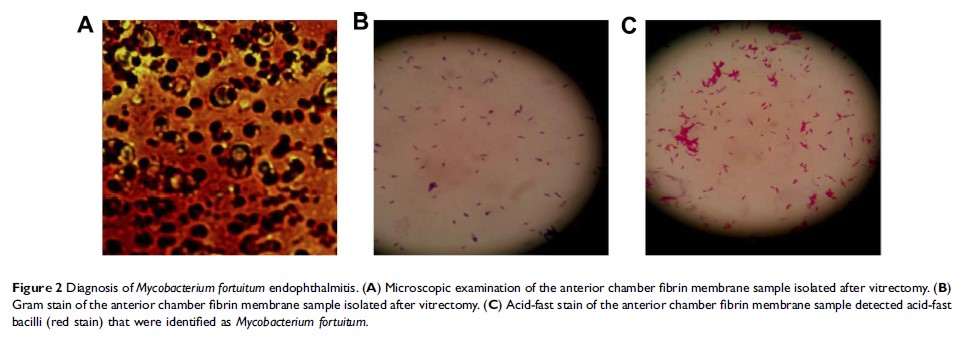
Background: Endophthalmitis caused by Mycobacterium fortuitum as a complication of cataract surgery is rare in China and globally. This study aimed to report the clinical features, surgical treatment strategies, antibiotic susceptibilities and treatment outcomes in patients with endophthalmitis caused by Mycobacterium fortuitum .
Patients and methods: A case series of 15 patients (15 eyes) with post-cataract endophthalmitis caused by Mycobacterium fortuitum treated at the Ophthalmology Clinic of Shengjing Hospital between June 2008 and June 2017 was reviewed retrospectively. Information about Mycobacterium fortuitum culture results, clinical features, surgical procedures, and final visual acuity were obtained.
Results: The vitreous samples were all positive. These eyes underwent total capsulectomy and intraocular lens explantation and vitrectomy combined with intravitreal and intravenous injections of antibiotics. Finally, 14 eyes had controlled inflammation and retained eyeballs. One eye had panophthalmitis and enucleation of the eyeball. Presenting visual acuity ranged from counting fingers to no light perception. Final visual acuity was better than 20/400 in 4 of 15 eyes (26.67%), 20/400 to hand motions in 7 of 15 eyes (46.67%), and light perception to no light perception in 4 of 15 eyes (26.67%) at 6-month follow-up visit.
Conclusion: Mycobacterium fortuitum might be an etiologic agent in postoperative endophthalmitis. The Mycobacterium fortuitum endophthalmitis might be treated with early vitrectomy and targeted antibiotic therapy approach.
Keywords: Mycobacterium fortuitum , vitrectomy, post-cataract, endophthalmitis