110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

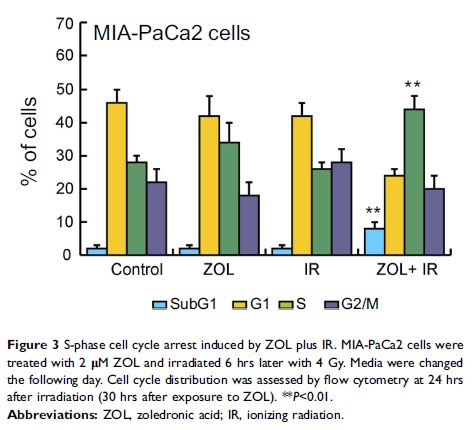
唑来膦酸通过 STAT3/NF-κB 信号传导失活在人胰腺癌细胞中表现出放射增敏活性
Authors You Y, Wang Q, Li H, Ma Y, Deng Y, Ye Z, Bai F
Received 22 January 2019
Accepted for publication 9 April 2019
Published 4 June 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 4323—4330
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S202516
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Aruna Narula
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Takuya Aoki
Background: Although pancreatic cancer is typically radio-sensitive, local treatment failure and metastasis are commonly caused by the development of resistance to radiotherapy. In the current study, the radio-sensitizing actions of zoledronic acid (ZOL) on pancreatic cancer cells were investigated.
Materials and methods: Three human pancreatic cancer cell lines were exposed to ZOL, ionizing radiation (IR), or a combination of both, and the effects of the respective drug regimens on cell proliferation and invasion were examined.
Results: Combined treatment with low doses of ZOL plus IR efficiently increased cell death and attenuated cell invasion compared with the individual use of ZOL or IR. These effects of ZOL were associated with inactivation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) and nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB).
Conclusion: Collectively, these data suggest that ZOL in combination with IR is a promising therapeutic strategy for enhancing radio-sensitivity in pancreatic cancer cells via downregulation of the STAT3/NF-κB signaling pathway.
Keywords: pancreatic cancer, radio-resistance, zoledronic acid, radio-sensitizing effects