110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

通过采用术后快速康复方法改善内镜鼻窦手术的围手术期生活质量
Authors Wu X, Kong W, Zhu Q, Wang W, Xu H, Zhou S, Yang Q
Received 27 December 2018
Accepted for publication 8 April 2019
Published 4 June 2019 Volume 2019:15 Pages 683—688
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/TCRM.S199630
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Justinn Cochran
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Deyun Wang
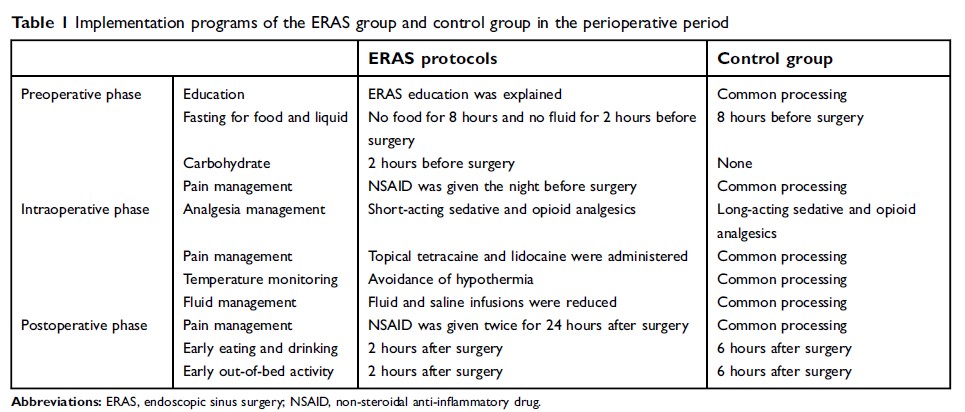
Background: Endoscopic sinus surgery (ESS) has been the definitive treatment for chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS), but the complications caused perioperatively may affect patients’ quality of life (QoL). This study aims to evaluate the effects of enhanced recovery after surgery (ERAS) on improving perioperative QoL in ESS.
Materials and methods: Seventy-four patients with chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (CRSwNP) met the criteria for inclusion. Participants undergoing ESS were randomly divided into an ERAS group and a control group, and QoL assessment was performed using the Chinese version of the 22-item Sinonasal Outcomes Test (SNOT-22). Measurements were administered at baseline, and on postoperative day 1 (POD1), POD3 and POD6. Complications such as nausea/emesis, hemorrhage, aspiration and dizziness were also recorded.
Results: The preoperative global SNOT-22 scores (mean ± SD) were 39.89±4.86 in the ERAS group and 40.52±3.61 in the control group (t =0.643, P =0.522). On POD1, the global SNOT-22 scores increased significantly to 51.77±5.59 and 62.02±3.86 (t =9.218, P <0.01), and on POD3 they increased to 48.22±6.22 and 51.11±5.14, respectively (t =2.179, P <0.05). However, the scores recovered to 39.39±4.73 and 40.13±3.31 in the respective groups on POD6, which were lower than but not statistically significant different from the baseline (t =0.786, P =0.434). There were statistically significant improvements across all subdomains of SNOT-22 for patients in the two groups only in POD1 (all P <0.05). The ERAS group did not have an increased incidence of complications such as nausea/emesis (χ 2=0.223, P >0.05), hemorrhage, aspiration and dizziness compared to the control group.
Conclusion: ERAS could improve perioperative QoL in patients with CRSwNP undergoing ESS, and SNOT-22 can be used for ERAS evaluation as a patients’ outcome report.
Keywords: chronic rhinosinusitis, enhanced recovery after surgery, quality of life, SNOT-22