110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

NETO2 通过激活 STAT3 信号通路促进胰腺癌细胞增殖、侵袭和迁移
Authors Li YX, Zhang YP, Liu JS
Received 5 February 2019
Accepted for publication 15 April 2019
Published 6 June 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 5147—5156
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S204260
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Chien-Feng Li
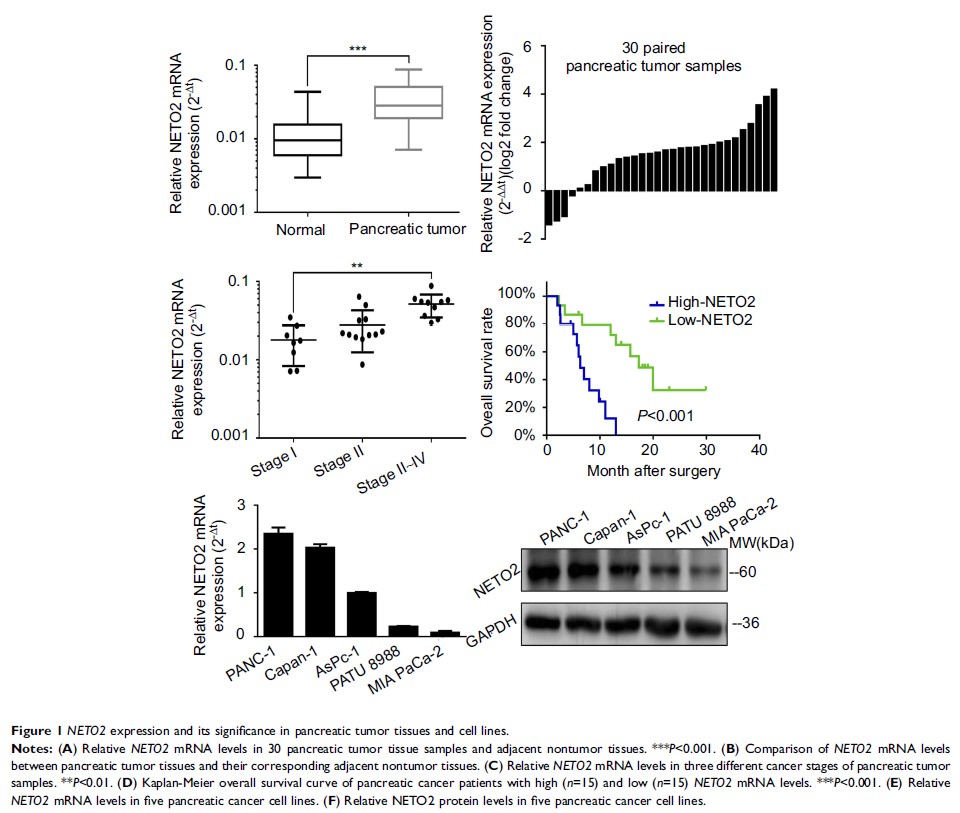
Purpose: The biological functions of neuropilin and tolloid-like 2 (NETO2 ) in the progression of pancreatic cancer remained unexplored. We aimed to investigate the biological roles and underlying molecular mechanisms of NETO2 in pancreatic cancer.
Materials and methods: Thirty paired pancreatic tumor tissue samples and corresponding nontumor tissues were obtained from 30 pancreatic cancer patients who did not receive preoperative chemotherapy or radiotherapy. The changes in multiple cellular functions associated with tumor progression were assessed after NETO2 knockdown/overexpression in pancreatic cancer cell lines. Additionally, a mouse-xenograft model was developed to verify the in vitro results.
Results: NETO2 was upregulated in pancreatic tumor tissues. Elevated expression of NETO2 was not only associated with an advanced tumor stage, but was also a prediction of poor prognosis for pancreatic cancer patients. Knockdown of NETO2 in pancreatic cancer cell lines arrested the cell cycle and inhibited cell proliferation, colony formation, invasion, and migration; in contrast, overexpression of NETO2 had an opposite effect on all of these parameters. A STAT3 specific inhibitor, cryptotanshinone, reversed the tumor-promoting effects induced by NETO2 overexpression in pancreatic cancer. Western blot analysis showed that invasion and migration were closely related to epithelial–mesenchymal transition, and that the STAT3 signaling pathway was involved in NETO2 -mediated oncogenic transformation in pancreatic cancer cells. Furthermore, NETO2 knockdown significantly inhibited the growth of pancreatic tumor xenografts in nude mice.
Conclusion: NETO2 has an important role in the progression and metastasis of pancreatic cancer and could serve as a novel candidate for targeted therapy of pancreatic cancer.
Keywords: pancreatic cancer, NETO2 , proliferation, metastasis, STAT3