110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

ELF-1 在鼻咽癌中的表达通过调节 CCL2/CCR2 信号传导促进癌细胞的增殖和转移
Authors Chen CH, Su LJ, Tsai HT, Hwang CF
Received 28 November 2018
Accepted for publication 16 April 2019
Published 6 June 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 5243—5254
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S196355
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Andrew Yee
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Antonella D'Anneo
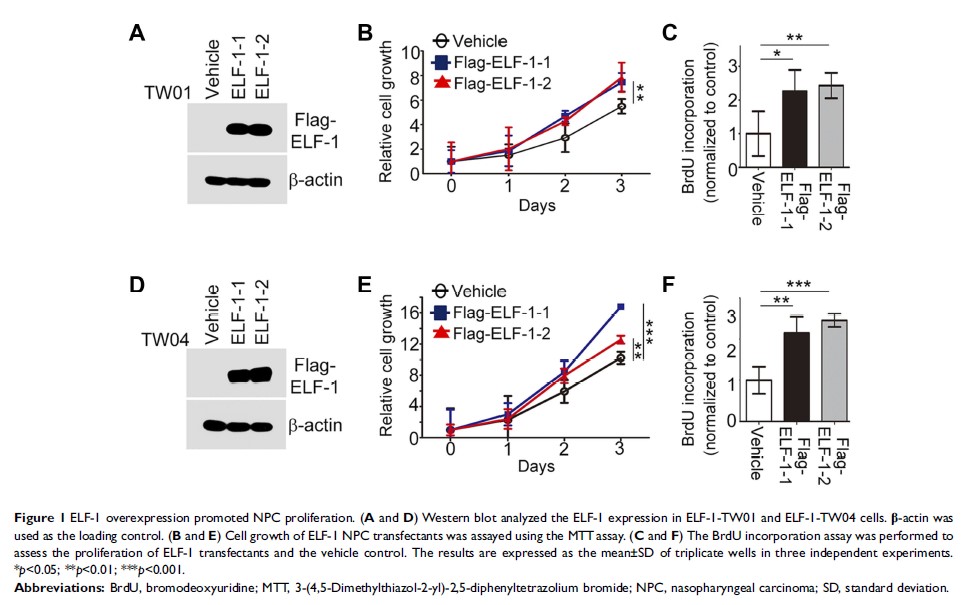
Background: Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) is a prevalent malignant tumor in Southeast Asia. The management of NPC has remained a challenge until now. ELF-1 is a member of the ETS family of transcription factors that regulate genes involved in cellular growth. ELF-1 expression has been reported in various cancers and is required for tumor growth and angiogenesis; however, its function in NPC remains unclear. In the present study, we characterized the role and underlying mechanism of ELF-1 in NPC.
Methods: The biological functions of ELF-1 in NPC cells such as proliferation, migration, invasion, and drug resistance were investigated using MTT, BrdU incorporation, and Transwell assays. To gain more insight into the mechanism of ELF-1 in NPC, we analyzed CCL2/CCR2 signaling by Western blotting, ELISA, siRNAs, and CCR2 antagonist.
Results: Gain-of-function of ELF-1 in TW01 and TW04 cells promoted NPC cell proliferation, BrdU incorporation, migration, invasion and cisplatin resistance. By contrast, knockdown of ELF-1 produced opposite results. Overexpression of ELF-1 enhanced the expression of CCL2 via binding to its promoter region and increased the level of the extracellular matrix protein CCL2 in cell culture medium. ELF-1 expression also modulated the downstream targets of CCL2/CCR2 signaling. Most importantly, ELF-1-induced NPC malignant phenotypes were abrogated by a CCR2 inhibitor, implying that the CCL2/CCR2 signaling axis was involved in ELF-1-mediated regulation in NPC.
Conclusion: Our data suggest that ELF-1 plays an oncogenic role in NPC development associated with the CCL2/CCR2 signaling pathway and may therefore be a potential target for NPC therapy.
Keywords: ELF-1, NPC, CCL2