110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

基于人类学习行为的电子商务社会网络服务效能的智能影响因素之实证分析
Authors Zhang K, Xu Y, Liu W
Received 26 January 2019
Accepted for publication 26 April 2019
Published 11 June 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 417—425
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/PRBM.S203007
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Justinn Cochran
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Igor Elman
Background: It is crucial for companies to understanding users’ choices and learning behaviors, and the corresponding influencing factors and cognitive patterns regarding social network services to communicate with potential customers.
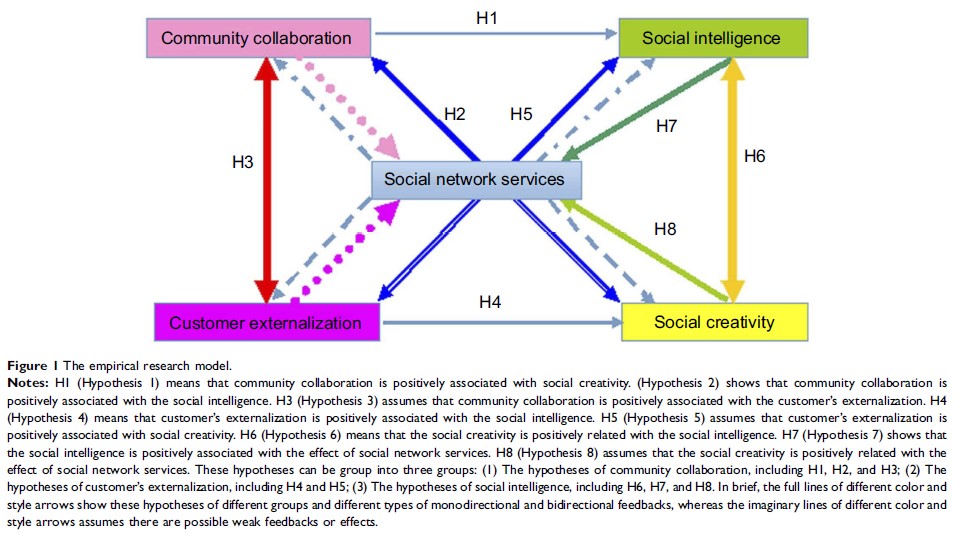
Methods: In this study, a casual structural model was constructed and developed to model and characterize the relationships between problems to be resolved as antecedent variables and success factors as consequent variables with the intermediary variables based on human learning behaviors, whereas the concept of social network service was introduced to summarize the current issues of social network services and empirically factors affecting effectiveness of social network services.
Discussion: This study highlighted the corporate need to examine the intelligent role and learning effectiveness of social network services when studying social creativity and intelligence in a social networking environment. Firstly, the framework and hypotheses of social network services were introduced to summarize the current issues of social network services and the main influencing factors affecting the working patterns of social network services. Subsequently, the empirically established model was further tested to explore the possible meaningful relationships among those variables used.
Results: The study revealed that the social network services provider and the customer should improve their social creativity and community collaboration; these could be expanded and enhanced by increasing the social intelligence to raise the social network services’ effect and the customer’s externalization. Furthermore, social intelligence, community collaboration, and customer externalization were factors significantly influencing customers’ social creativity, while the customer externalization and community collaboration were the two important factors affecting social intelligence.
Conclusion: The study implied that social network services providers should provide more and more intelligent and inspiring services for their customers.
Keywords: empirical analysis, computational modeling, intelligent influence factor, social network services, human learning behaviour