110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

假基因 DUXAP10 作为诊断和预后标志物,通过激活肝细胞癌中的 PI3K/AKT 通路促进细胞增殖
Authors Yue C, Liang C, Ge H, Yan L, Xu Y, Li G, Li P, Wei Z, Wu J
Received 30 March 2019
Accepted for publication 16 May 2019
Published 11 June 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 4555—4566
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S210623
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Shreya Arora
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr William Cho
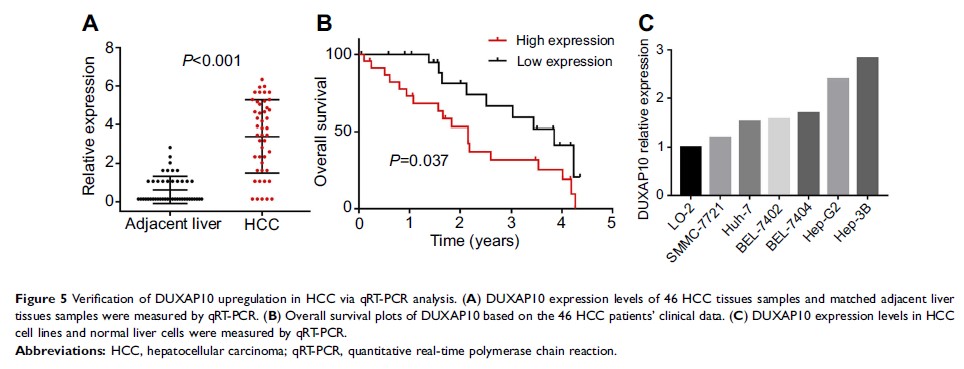
Background: Recently, the pseudogene DUXAP10 was shown to be overexpressed in various human cancers and emerged as a key cancer regulator. However, the roles of DUXAP10 in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) tumorigenesis and progression remain uncharacterized.
Methods: Comprehensive analyses were performed to investigate DUXAP10 expression patterns, potential biologic functions, and clinical significance in HCC based on the data downloaded from the Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) and Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) databases. DUXAP10 expression levels in HCC tissue sections and cells were verified using quantitative real-time PCR analysis. DUXAP10-siRNA was used to silence DUXAP10 in the Hep3B cell line to determine the roles of DUXAP10 in HCC cell proliferation.
Results: DUXAP10 was significantly overexpressed in HCC, and DUXAP10 upregulation was closely associated with poor prognoses in HCC patients. DUXAP10 knockdown decreased cell proliferation and arrested HCC cells in the G1 phase of the cell cycle. Western blot analysis showed that DUXAP10 knockdown decreased p -AKT expression in HCC cells.
Conclusion: Our study demonstrates that pseudogene DUXAP10 promotes HCC cell proliferation by activating PI3K/AKT pathway and could act as a potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for HCC patients.
Keywords: DUXAP10, HCC, biomarker