110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

对多西他赛耐药的、亲代人乳腺癌细胞外泌体中失调的 microRNAs 的生物信息学分析
Authors Chen WX, Xu LY, Cheng L, Qian Q, He X, Peng WT, Zhu YL
Received 12 January 2019
Accepted for publication 30 April 2019
Published 12 June 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 5425—5435
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S201335
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Rituraj Purohit
Background: Resistance to docetaxel is a major obstacle to effective treatment of breast cancer. Exosomal microRNAs (miRNAs) have recently been introduced in cell-to-cell transmission of chemoresistance between heterogeneous populations of tumor cells with diverse drug sensitivity. However, a systematic evaluation of the exosomal miRNA signature remains largely unclear.
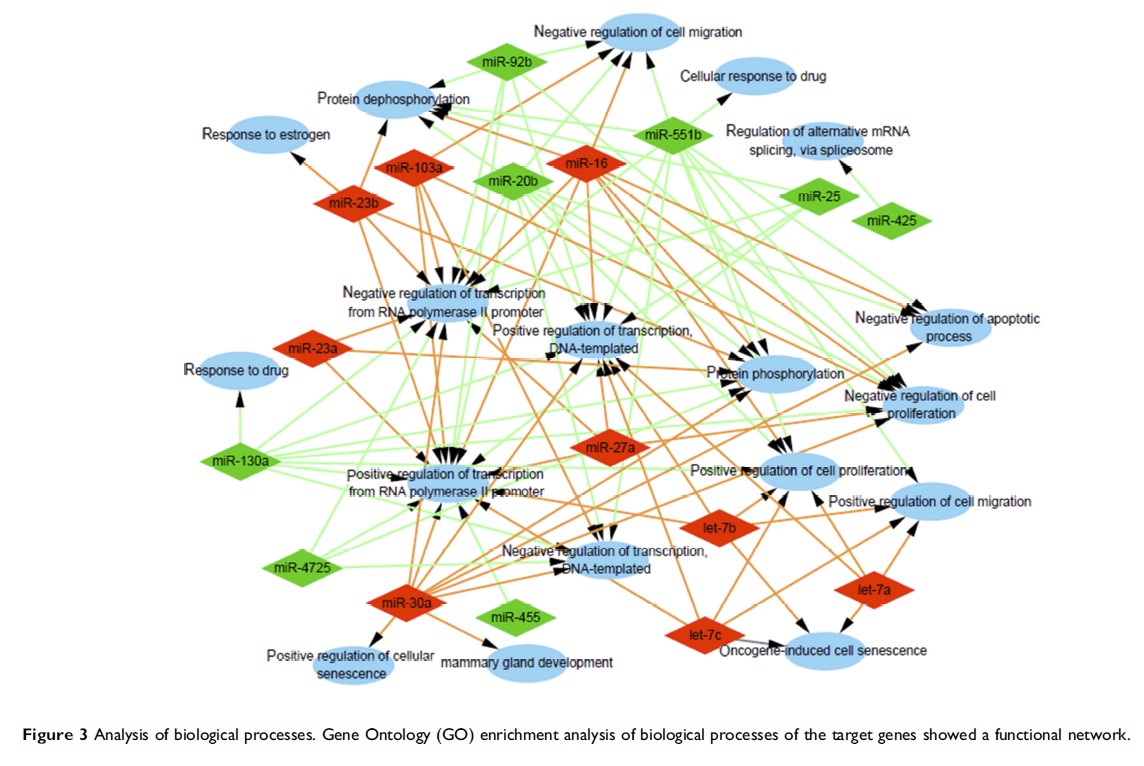
Method: miRNA expression profiles in exosomes from docetaxel-resistant (D/exo) and parental sensitive breast cancer cells (S/exo) were assessed using microarray. Bioinformatics analysis was performed to predict target genes of the dysregulated miRNAs and to uncover their potential roles in chemoresistance formation. Signaling pathways, gene ontology terms, transcription factors, protein–protein interactions, and hub genes were also constructed.
Results: The selected exosomal miRNAs could modulate target genes responsible for MAPK, TGF-beta, Wnt, mTOR, and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways. Function enrichment analysis revealed the involvement of target genes in transcription regulation, protein phosphorylation, kinase activity, and protein binding. Enriched transcription factors including SP1, SP4, and EGR1 were obtained and a protein–protein interaction network was established. The hub genes for up-expressed and down-expressed exosomal miRNAs such as CCND1 and PTEN were identified.
Conclusion: This bioinformatics study provides a comprehensive view of the function of dysregulated exosomal miRNAs, and may help us to understand exosome-mediated resistance transmission and overcome docetaxel resistance in future breast cancer therapy.
Keywords: breast cancer, exosomes, microRNA, chemoresistance, docetaxel