110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

指定的较高水平血尿酸可能对 60 岁以上中国人群的骨密度有保护作用:来自中国东北的一项横断面研究
Authors Chen F, Wang Y, Guo Y, Wang J, Yang A, Lv Q, Liu Y, Ma G, Liu Y, Wang D
Received 5 September 2018
Accepted for publication 17 February 2019
Published 12 June 2019 Volume 2019:14 Pages 1065—1073
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CIA.S186500
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Zhi-Ying Wu
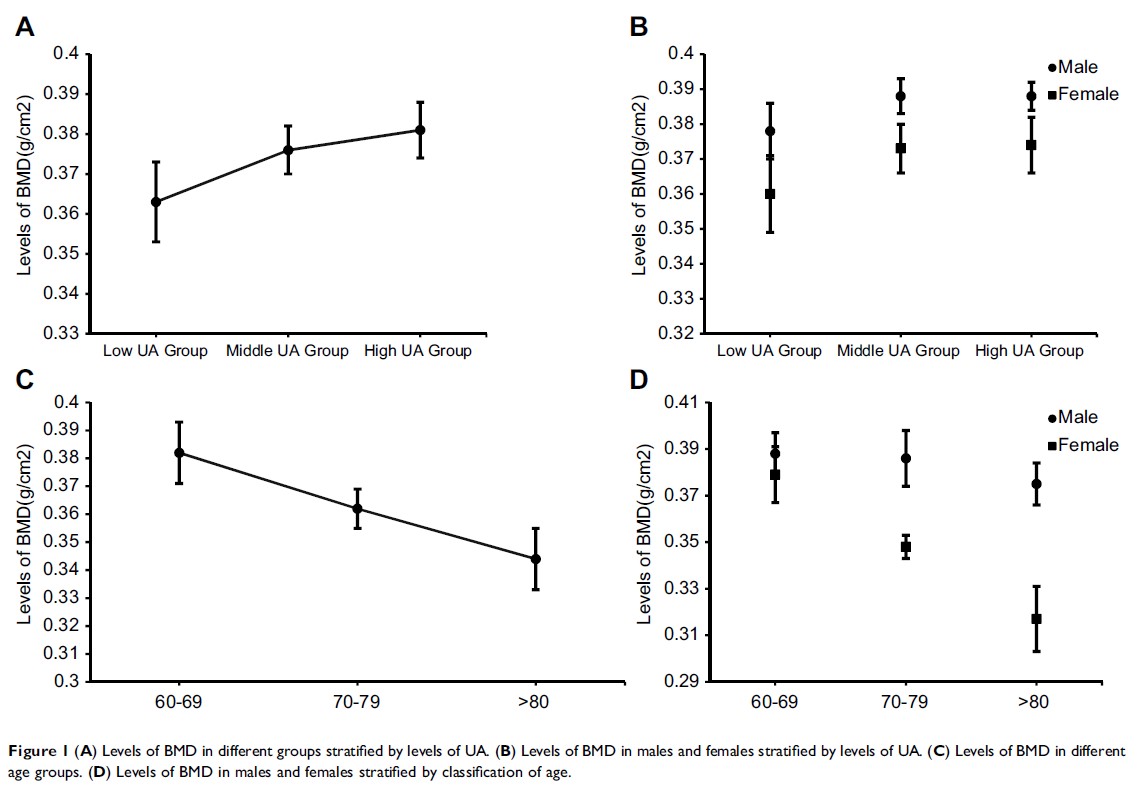
Background and objective: Oxidative stress has been demonstrated to be a mechanism that leads to bone mass reduction, and according to many studies, serum uric acid (UA) is a strong endogenous antioxidant that can protect bone mineral density (BMD). To date, there have been no large-scale, cross-sectional studies based on the population in northeast China to assess the relationship between serum UA and BMD. Therefore, we examined the association between serum UA and BMD among a Chinese population older than 60 years old in northeast China.
Methods: This research was a cross-sectional study of 3465 Chinese individuals over 60 years old in nine communities from the city of Shenyang, which is the capital of northeast China’s Liaoning Province. Participants were stratified into three groups by serum UA or BMD levels, and then Pearson’s correlation analysis and multiple regression analysis were used to study the relationship between serum UA and BMD.
Results: We found that participants with higher serum UA levels had significantly greater BMD and T-values compared to those of participants with lower serum UA levels. After adjusting for confounding factors, Pearson’s correlation analysis and multiple regression analysis showed that higher serum UA levels remained associated with higher BMD levels (P <0.05). In different models, the prevalence of osteoporosis (OP) among participants with higher serum UA levels was reduced by 23% to 26% (P <0.05) compared to that in individuals with lower serum UA levels. In addition, serum UA levels were negatively correlated with estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) and positively correlated with 25-hydroxy vitamin D3 [25-(OH)D3] (P <0.05).
Conclusion: We concluded that higher serum UA levels are associated with greater BMD, and serum UA might have a protective effect on bone metabolism due to its antioxidant properties.
Keywords: serum uric acid, bone mineral density, osteoporosis