110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

SNHG1 通过调节乳腺癌中的 miR-382 促进增殖和侵袭
Authors Zheng S, Li M, Miao K, Xu H
Received 18 December 2018
Accepted for publication 22 April 2019
Published 18 June 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 5589—5598
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S198624
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Ahmet Emre Eskazan
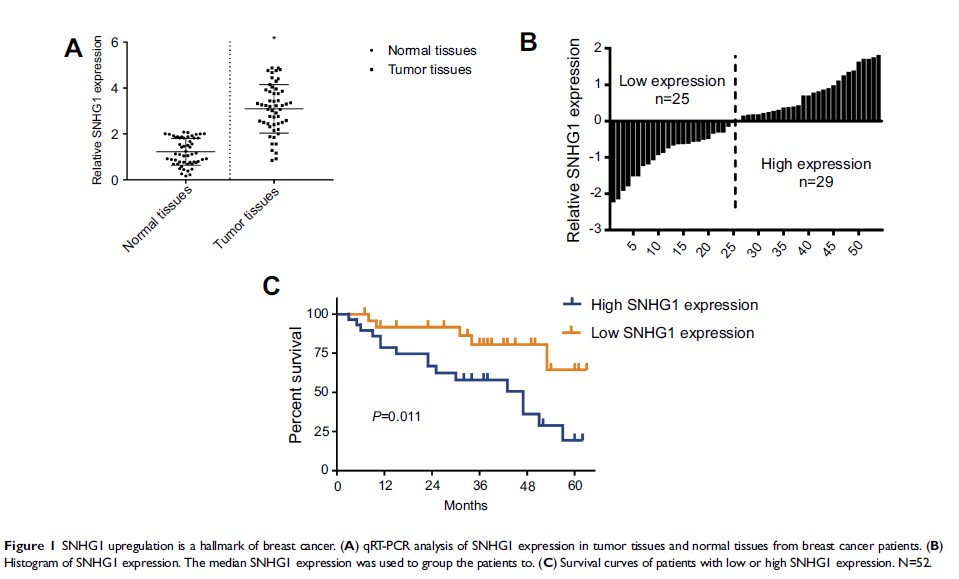
Introduction: Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are key regulators in multiple cancers. lncRNA, SNHG1, was shown to be associated with tumorigenesis. However, little is known about the role SNHG1 plays in breast cancer. The aim of the study was to study the role and underlying mechanism of SNHG1 regulation in breast cancer.
Methods: Quantitative real-time PCR was used to measure the levels of SNHG1, miR-382 and ZEB1 levels in breast cancer tissue or cells. The proliferation, colony formation, migration and invasion of breast cancer cells, under SNHG1 knockdown achieved by transfection of SNHG1-specific siRNAs, were assessed by Cell Counting Kit-8, colony forming, scratch wound and transwell assays. Bioinformatical analysis and luciferase assay were used to explore the interaction between SNHG1 and its potential miRNA target. Western blot was used to evaluate the expression of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) markers. MDA-MB-231 cells with or without SNHG1 knockdown were used to initiate tumor xenografts in vivo. Tumor growth and expression of SNHG1, miR-382-5p and EMT markers were evaluated.
Results: SNHG1 upregulation was observed in breast cancer tissues and cells. Knockdown of SNHG1 attenuated breast cancer proliferation, colony formation, migration and invasion. A miRNA, miR-382-5p, was identified as the target of SNHG1. A reciprocal negative regulation was found between SNHG1 and miR-382-5p. SNHG1 knockdown attenuated EMT both in vitro and in vivo. miR-382-5p transfection reversed the tumor-promoting role by SNHG1. In vivo, SNHG1 knockdown decreased breast tumor growth.
Conclusion: SNHG1 promotes breast cancer through the regulation of miR-382-5p and EMT markers. Our results report SNHG1 as a novel miRNA that govern the progression of breast cancer, providing a potential new therapeutic target in breast cancer.
Keywords: breast cancer, therapeutic target, SNHG1, miR-382