110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

由干酪乳杆菌 ATCC 393 生物合成的硒纳米粒通过 Nrf2 信号传递介导的线粒体途径减轻由氧化应激引起的肠上皮屏障功能障碍
Authors Xu C, Qiao L, Ma L, Guo Y, Dou X, Yan S, Zhang B, Roman A
Received 21 December 2018
Accepted for publication 8 May 2019
Published 18 June 2019 Volume 2019:14 Pages 4491—4502
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S199193
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Mian Wang
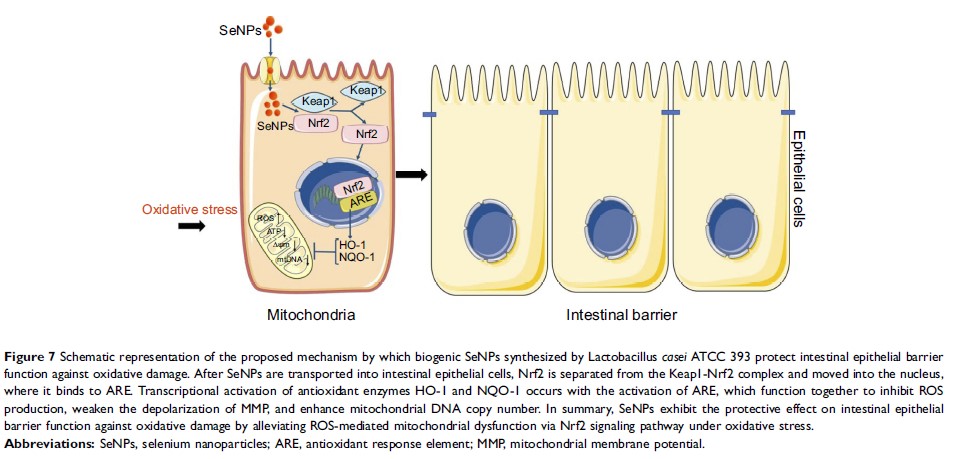
Background: Selenium (Se) can exert antioxidative activity and prevent the body from experiencing oxidative injury. Biogenic Se nanoparticles (SeNPs) synthesized by probiotics possess relatively strong chemical stability, high bioavailability, and low toxicity, this makes them potential Se supplements. Previously, we demonstrated that SeNPs synthesized by Lactobacillus casei ATCC 393 can alleviate hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)-induced human and porcine intestinal epithelial cells’ oxidative damage. However, the antioxidant mechanism remains unclear.
Methods: The possible antioxidant mechanism and protective effect of SeNPs on intestinal epithelial permeability and mitochondrial function were evaluated by establishing an H2O2-induced oxidative damage model of human colon mucosal epithelial cells (NCM460) and conducting Nrf2 inhibitor interference experiments. Mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP), mitochondrial DNA content, adenosine triphosphate (ATP), ROS, and protein expression levels of Nrf2-related genes were determined. Mitochondrial ultrastructure was visualized by transmission electron microscopy.
Results: An amount of 4 μg Se/mL of SeNPs synthesized by L. casei ATCC 393 alleviated increase of ROS, reduced ATP and MMP, and maintained intestinal epithelial permeability in NCM460 cells challenged by H2O2. In addition, SeNPs improved the protein levels of Nrf2, HO-1, and NQO-1. Moreover, SeNPs attenuated the damage of mitochondrial ultrastructure caused by oxidative stress. Nrf2 inhibitor (ML385) abolished the regulatory effect of SeNPs on intracellular ROS production.
Conclusion: Data suggest that biogenic SeNPs synthesized by L. casei ATCC 393 can protect the intestinal epithelial barrier function against oxidative damage by alleviating ROS-mediated mitochondrial dysfunction via Nrf2 signaling pathway. Biogenic SeNPs are an attractive candidate for potential Se supplement agent in preventing oxidative stress-related intestinal disease by targeting mitochondria.
Keywords: Lactobacillus casei , selenium nanoparticles, mitochondrial, antioxidant, reactive oxygen species, intestinal barrier