110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

免疫组化标志物和乳房密度的转换与接受新辅助化疗后未能达到病理完全反应的年轻乳腺癌患者的病理反应和预后相关
Authors Zhao Y, Wang X, Huang Y, Zhou X, Zhang D
Received 19 December 2018
Accepted for publication 16 May 2019
Published 20 June 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 5677—5690
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S198844
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Antonella D'Anneo
Purpose: Patients younger than age 35 that fail to achieve a pathologic complete response (pCR) after Neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NACT) tend to have worse long term outcomes. The purpose of our study was to assess the correlation between the conversion of immunohistochemical (IHC) markers and breast density and investigate their association with pathological response and prognosis.
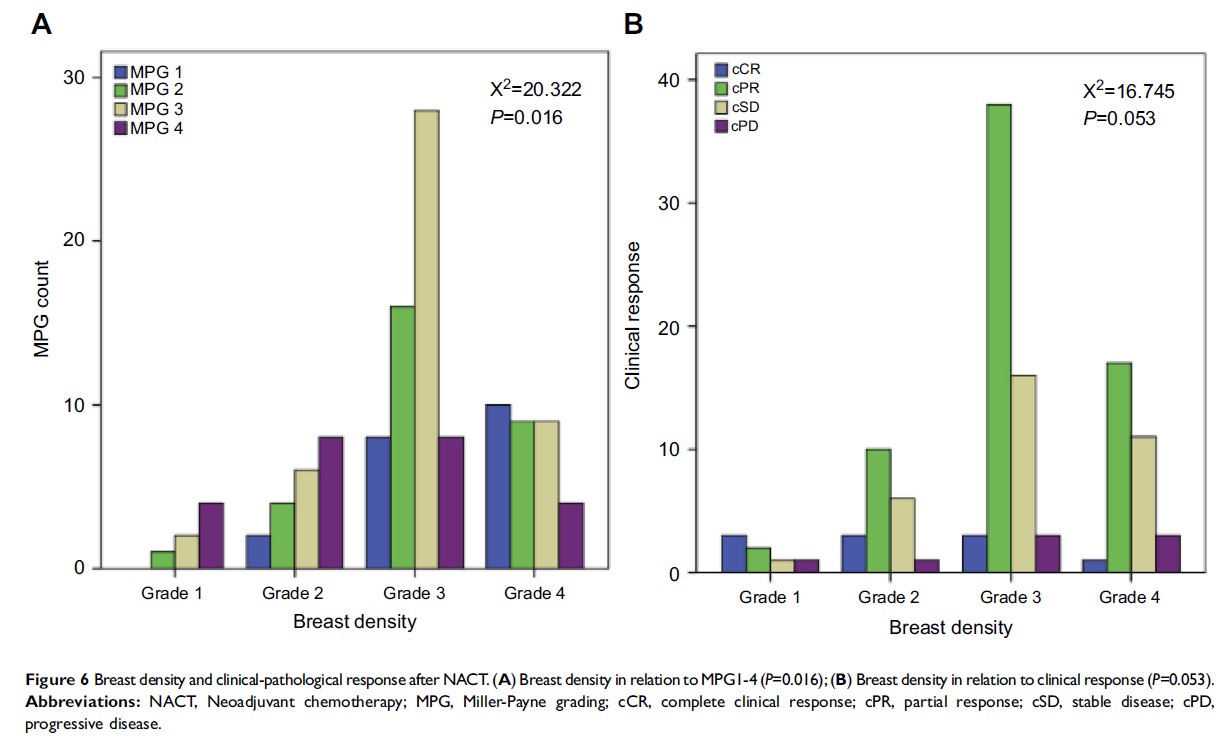
Methods: We included 119 patients younger than age 35 who failed to achieve a pCR after NACT in this analysis. We evaluated the clinical and pathological response to NACT by the Union for International Cancer control (UICC) and the Miller-Payne grading (MPG) systems, respectively. A breast density assessment was applied via mammography examination at the time of diagnosis. MPG and breast density (BD) have been combined to define a specific classification of three risk levels to evaluate the prognosis of these patients.
Results: The diameter changes of the tumors and lymph nodes were negatively associated with hormone receptor conversion and positively correlated with Ki67 conversion. A significantly large size change was observed in the groups demonstrating conversion from HER-2 (+) to (−). The variation level of IHC markers was related to MPG and BD and was associated with the survival rate of the patients. Patients with a high breast density and low Miller-Payne grading after NACT had a higher risk of distant metastases or local recurrences.
Conclusion: ER, PR and Ki67 conversion are closely related to MPG, while PR and Ki67 conversion are closely related to BD. While ER and PR conversion are independent and significant predictors of disease free survival (DFS) and overall survival (OS), HER-2 and Ki67 conversion are only significant for DFS. This risk factor grouping provides a useful index to evaluate the risk of young women with breast cancer who fail to achieve a pCR.
Keywords: young breast cancer, neoadjuvant chemotherapy, IHC markers, conversion, breast density, survival