110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

分子分型揭示了 pvl -阳性序列类型 22 甲氧西林敏感金黄色葡萄球菌在中国西北乌鲁木齐的出现
Authors Yuan W, Liu J, Zhan Y, Wang L, Jiang Y, Zhang Y, Sun N, Hou N
Received 25 January 2019
Accepted for publication 21 May 2019
Published 20 June 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 1719—1728
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IDR.S202906
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Professor Suresh Antony
Background: Staphylococcus aureus is among the most common causes of health care- and community-associated infections worldwide. The distributions of different S. aureus clones change over time and also vary geographically. The purpose of this study was to determine the molecular type and antimicrobial resistance profiles of clinical S. aureus strains isolated in Urumqi, Northwestern China.
Methods: A total of 605 clinical S. aureus isolates were collected from Xinjiang Military General Hospital, in Urumqi. Protein A-encoding (spa ) typing, multilocus sequence typing, staphylococcal chromosomal cassette mec typing, Panton-Valentine leucocidin (pvl ) gene detection, and antimicrobial resistance profiling were performed.
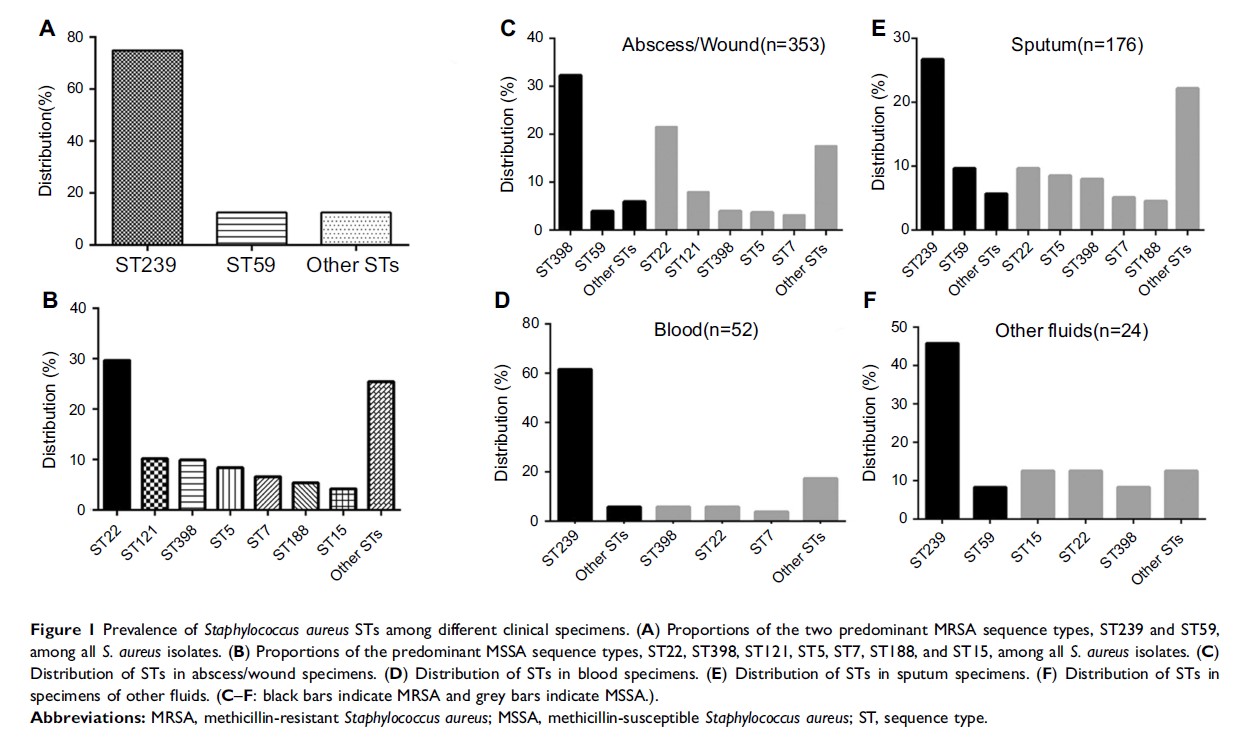
Results: Among these strains, 271 isolates (44.7%) were methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) and 334 (55.3%) were methicillin-susceptible S. aureus (MSSA). The MRSA strains consisted of 22 spa types and 14 sequence types (STs). ST239-MRSA-III-t030 (73.1%, 198/271) and ST59-MRSA-IV-t437 (11.8%, 32/271) were the most common, and ST22-MRSA-IV-t309 was the rarest (2.02%, 6/271). The MSSA strains consisted of 93 spa types and 29 STs. ST22, ST121, ST398, ST5, ST7, ST188, and ST15 were the main MSSA STs, and ST22-MSSA-t309 was most common (26.0%, 87/334). The pvl gene was present in 20.3% of all S.aureus strains, and 80.8% (88/99) of ST22-MSSA strains harbored the pvl gene. A total of 85.7% pvl -positive ST22-MSSA strains were spa t309 (85/99), and 87.5% of pvl -positive ST22-MSSA strains were from abscesses or wounds (skin and soft tissue infections). All ST239-MRSA strains were resistant to gentamicin (GEN), levofloxacin (LEV), ciprofloxacin (CIP), moxifloxacin (MXF), rifampicin (RIF), and tetracycline (TET). Among the ST59-MRSA strains, over 70.0% were resistant to erythromycin (ERY), clindamycin (CLI), and TET. ST22-MSSA remained susceptible to most antibiotics, but was resistant to PEN (97.0%), ERY (57.6%), and CLI (15.2%).
Conclusion: Our major results indicated that the antimicrobial resistance profiles and pvl genes of S. aureus isolates from Urumqi were closely associated with clonal lineage. ST239-MRSA-III-t030 and pvl -positive ST22-MSSA-t309 were the most common clones in this region of Northwestern China.
Keywords: Staphylococcus aureus, methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus , methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus , pvl gene, molecular typing