110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

枞酸通过阻断 IKKβ/NF-κB 信号传导抑制非小细胞肺癌细胞生长
Authors Liu X, Chen W, Liu Q, Dai J
Received 21 December 2018
Accepted for publication 3 April 2019
Published 20 June 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 4825—4837
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S199161
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Aruna Narula
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr XuYu Yang
Background: Abietic acid (AA) is one of the terpenoids, which are multifunctional natural compounds. It has been reported that AA possesses favorable therapeutic effects on inflammation and obesity.
Method: In the present study, we determined the inhibitory effect of AA on the proliferation and growth of non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cell lines for the first time. Then, flow cytometry and Western blot analysis were applied to determine the cell apoptosis and cell cycle. Finally, surface plasmon resonance, molecular docking and molecular dynamics (MD) simulation were performed to explore the underlying molecular mechanisms.
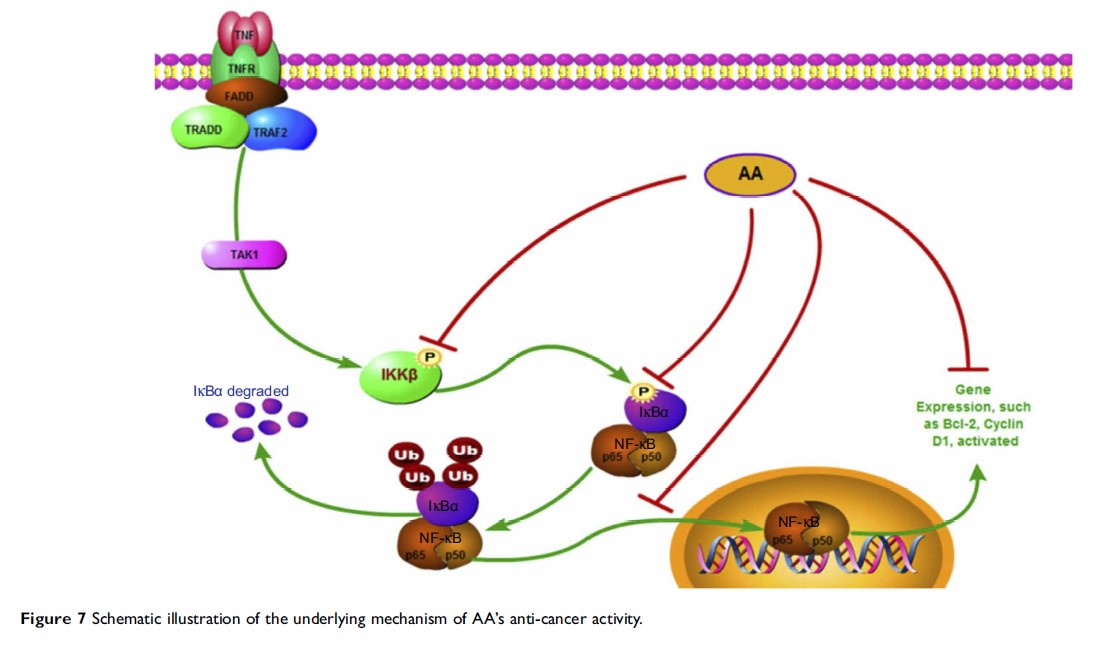
Results: In vitro experiments indicated that AA displays significant anti-proliferative, cell cycle arresting and pro-apoptotic activities. Mechanistically, AA abrogated tumor necrosis factor-α induced phosphorylation of IκB kinase (IKKα/β) (Ser176/180) and IkBα (Ser32), and inhibited the nuclear translocation of nuclear factor‐κB. Moreover, we found that the activities of AA against NSCLC cells were mediated by its IKKβ inhibition. Molecular docking and MD simulations demonstrated that the mechanism of action between AA and IKKβ was through hydrophobic interactions.
Conclusion: Our data indicate that AA could be a promising lead compound for the discovery of novel IKKβ inhibitors and potential agents for the treatment of NSCLC.
Keywords: abietic acid, hydrophobic interaction, IKKβ inhibitor, NSCLC