110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

MicroRNA-937 通过直接靶向和下调叉头框蛋白 Q1 来抑制乳腺癌的恶性表型
Authors Han X, Guo X, Zhang W, Cong Q
Received 4 March 2019
Accepted for publication 7 May 2019
Published 20 June 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 4813—4824
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S207593
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Rachel Predeepa
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Arseniy Yuzhalin
Purpose: Numerous microRNAs (miRNAs) are aberrantly expressed in breast cancer, and the dysregulation of miRNAs may affect the aggressiveness of this cancer. Aberrant expression of miRNA-937 (miR-937) in gastric and lung cancers has been reported, which plays tumor-suppressive or oncogenic roles in carcinogenesis including cancer progression. Our purpose was to investigate the involvement of miR-937 in breast cancer progression.
Patients and methods: The expression profile of miR-937 in breast cancer was assessed by reverse-transcription quantitative PCR. Biological effects of miR-937 upregulation on the malignant characteristics of breast cancer cells were determined in a series of functional experiments. The direct target of miR-937 in breast cancer cells was also identified.
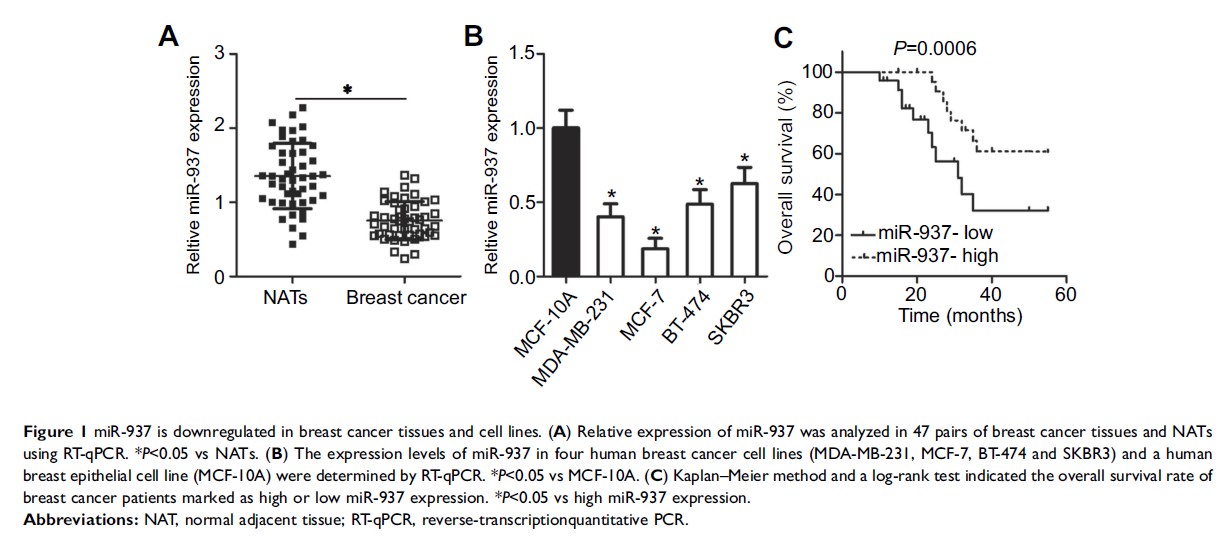
Results: Herein, the expression levels of miR-937 were notably lower in breast cancer, and its underexpression was significantly correlated with lymph node metastasis and TNM stage. Patients with breast cancer underexpressing miR-937 showed shorter overall survival than did patients with breast cancer overexpressing miR-937. Proliferation, migration, and invasiveness of breast cancer cells were evidently suppressed by miR-937 upregulation. In addition, ectopic miR-937 expression hindered breast cancer tumor growth in vivo. Forkhead box Q1 (FOXQ1 ) mRNA was found to be a direct target of miR-937 in breast cancer. FOXQ1 turned out to be overexpressed in breast cancer tissues, and its overexpression negatively correlated with miR-937 expression. Moreover, silencing of FOXQ1 recapitulated the tumor-suppressive effects of miR-937 overexpression on breast cancer cells. Notably, FOXQ1 restoration abrogated the miR-937-mediated suppression of proliferation, migration, and invasiveness of breast cancer cells.
Conclusion: These results collectively revealed that miR-937 acts as a tumor suppressor in breast cancer and restrains cancer progression by directly targeting FOXQ1 mRNA. These data suggest that targeting of the novel miR-937–FOXQ1 axis is an attractive therapeutic method against breast cancer.
Keywords: breast cancer, microRNA-937, forkhead box Q1