111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

IL-6 水平与重度抑郁症患者的睡眠障碍有关
Authors Wang M, Wei J, Yang X, Ni P, Wang Y, Zhao L, Deng W, Guo W, Wang Q, Li T, Ma X
Received 21 January 2019
Accepted for publication 6 May 2019
Published 27 June 2019 Volume 2019:15 Pages 1695—1700
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S202329
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Prof. Dr. Roumen Kirov
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Jun Chen
Purpose: Major depression disorder (MDD) was associated with inflammatory processes, but association results of inflammatory syndrome and MDD were inconsistent. To provide more evidence, we measured the plasma levels of IL-1β, IL-6, interferon (INT)-α2, INT-γ, and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α in patients having MDD and explored correlations between the five proinflammatory cytokines and specific depressive symptoms.
Patients and methods: Plasma concentrations of IL-1β, IL-6, INT-α2, INT-γ, and TNF-α were measured using ELISA for 44 MDD patients and 54 healthy controls. Patients with MDD were assessed on the 17-item Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (HAMD-17), and a total score and five syndrome scores were acquired.
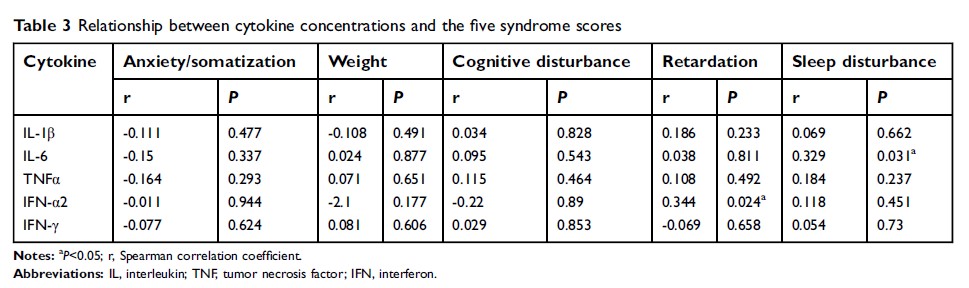
Results: IL-6 levels in depressed patients were significantly elevated than in healthy controls, but no significant differences were observed in the levels of INF-α2, INF-γ, IL-1β, or TNF-α. In addition, correlation analysis revealed that sleep disturbances positively correlated with IL-6. Although there was no significant difference between the two groups in the levels of INF-α2, a significant positive correlation between IFN-α2 and retardation was observed.
Conclusion: Elevated IL-6 levels were observed in MDD patients and IL-6 may correlate with sleep disturbances.
Keywords: major depression disorder, inflammation, cytokine, interleukin-6, sleep disturbances