111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

Atractylon 诱导细胞凋亡、遏制肝癌细胞转移并抑制体内生长
Authors Cheng Y, Chen T, Yang X, Xue J, Chen J
Received 15 November 2018
Accepted for publication 12 May 2019
Published 28 June 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 5883—5894
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S194795
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Professor Lu-Zhe Sun
Background: Hepatic cancer is the most common primary liver malignancy, with high incidence and mortality worldwide. Atractylon is an active constituent isolated from Atractylodes lancea (Thunb.) DC. and Atractylodes chinensis (DC.) Koidz., which proved to have multiple activities.
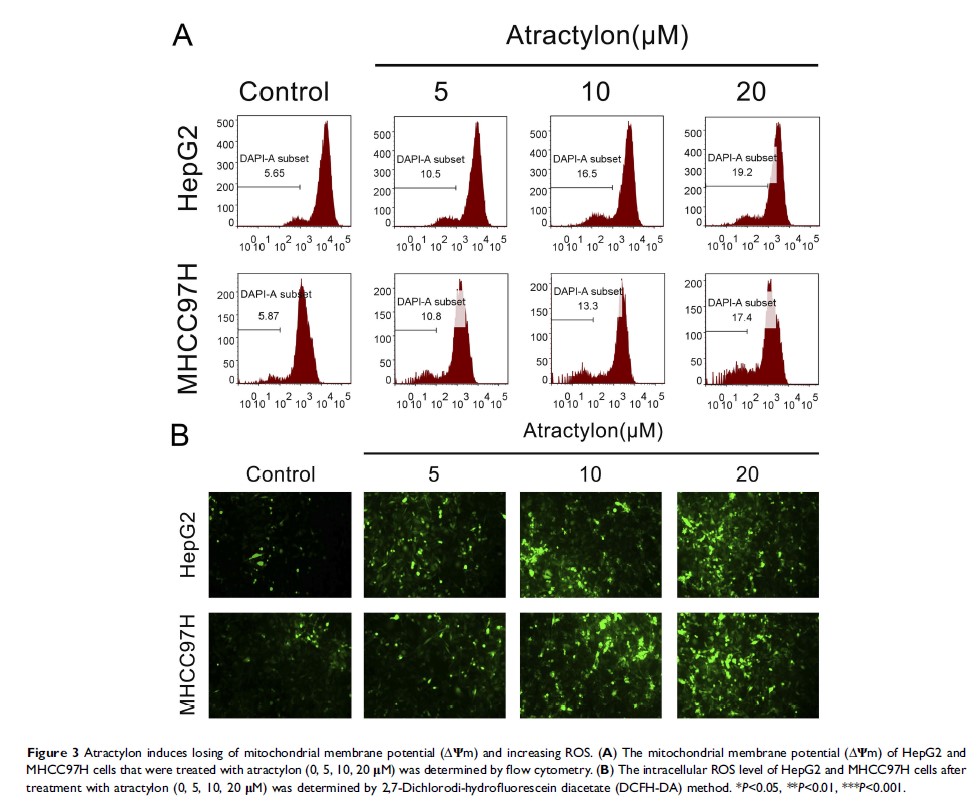
Methods: In this study, we evaluated the antihepatic cancer (HCC) effect of atractylon in vitro and in vivo and investigated its underlying mechanism. Cell proliferation, colony formation, cell apoptosis, migration and invaison and was identified by MTT, crystal violet staining, flow cytometry analysis, and Transwell assay. The ∆Ψm of HepG2 and MHCC97H cells were detected by Rhodamine 123. The ROS level was determined by 2,7-Dichlorodi-hydrofluorescein diacetate (DCFH-DA) method. Protein expression was identified by Western blot analysis. The anti-HCC effect of atractylon in vivo was evaluated by a subcutaneous tumor model.
Results: The results suggested that atractylon significantly inhibits the proliferation and promotes apoptosis of hepatic cancer cell lines, including HepG2, SMCC7721, and MHCC97H. Moreover, the results showed that atractylon reduces the mitochondrial membrane potential (∆Ψm), increases ROS level, inhibits the expression of Bcl-2, and promotes the expression of Bax and cleaved caspase-3, indicating that atractylon induces HCC apoptosis through the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway. Our results also demonstrated that atractylon inhibits migration and invasion of hepatic cancer cells by inhibiting the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) process and downregulating MMP-2 and MMP-9 expression. In addition, atractylon inhibited the growth of hepatic cancer and showed an inhibition effect on EMT process in vivo.
Conclusion: In all, this study suggested that atractylon showed a promising anti-HCC effect with inhibiting proliferation, inducing apoptosis, and blocking invasion in vitro and inhibiting growth in vivo.
Keywords: hepatic cancer, atractylon, migration, apoptosis, EMT