111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

人参皂甙 Rb1 预处理可逆转急性固定应激大鼠海马 BDNF/TrkB mRNA 和蛋白的变化
Authors Kang X, Hong W, Xie K, Tang H, Tang J, Luo S, Geng W, Jia D
Received 12 January 2019
Accepted for publication 14 May 2019
Published 1 July 2019 Volume 2019:13 Pages 2127—2134
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S201135
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Palas Chanda
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Anastasios Lymperopoulos
Purpose: Episodes of acute emotional or physical stress can have significant adverse effects on the hippocampus. Ginsenoside Rb1, the most predominant ginsenoside present in Panax species, has been reported to show a neuroprotective effect. The purpose of this study was to investigate the influence of ginsenoside Rb1 on plasma corticosterone (CORT) and adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) levels and hippocampal brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and tyrosine kinase B (TrkB) levels in rats subjected to acute immobilization stress.
Methods: Wistar rats were divided into controls treated with saline only (N), rats exposed to stress only (M), and rats pretreated with Rb1 (40 mg.kg (−1)) thirty minutes prior to stress exposure (R). In the model, animals were restrained in a plastic immobilizer for 2 h of acute immobilization stress at room temperature. ELISA was used to determine plasma levels of CORT and ACTH. The effect of Rb1 pretreatment on the expression of BDNF and TrkB was determined by immunofluorescence, real-time PCR, and Western blotting analysis.
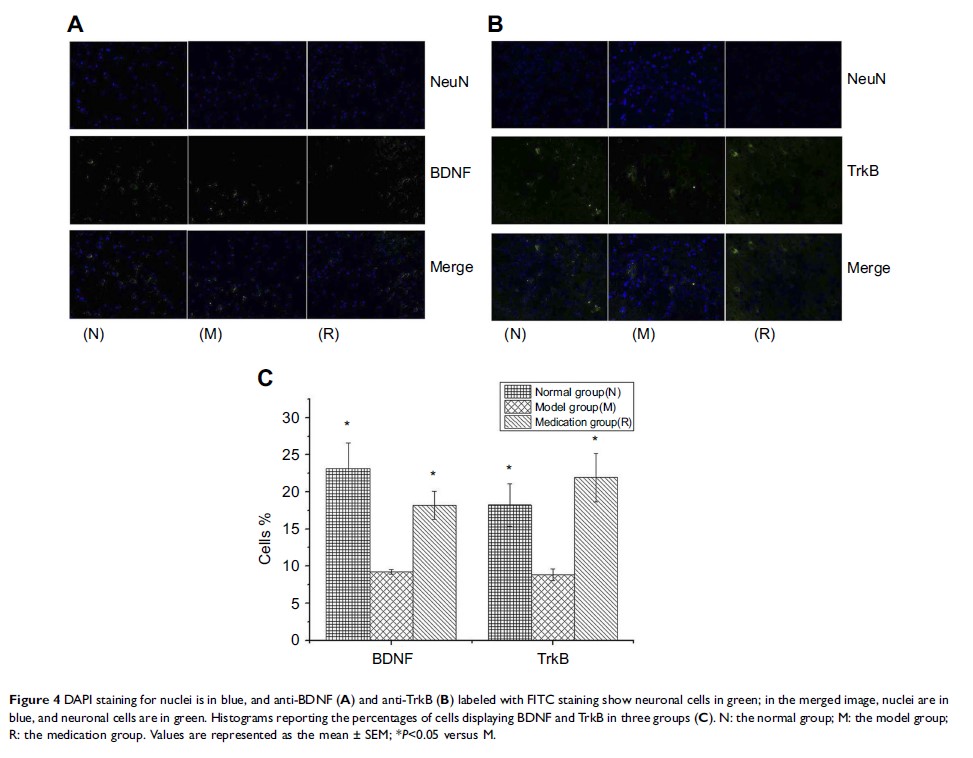
Results: The R group showed significantly increased plasma CORT and ACTH levels compared to the N and M groups. Acute stress stimulation suppressed BDNF and TrkB protein and mRNA expression in the hippocampus; otherwise, Rb1 pretreatment reversed the decreases.
Conclusion: The results from this study demonstrate that Rb1 pretreatment reverses the decreases in hippocampal BDNF/TrkB and increases the plasma levels of CORT and ACTH, indicating a potential neuroprotective effect of Rb1 against acute stress.
Keywords: ginsenoside Rb1, CORT; ACTH, acute immobilization stress, BDNF, TrkB