111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

肝细胞癌分子遗传靶标和关键通路的生物信息学分析
Authors Tu J, Chen J, He M, Tong H, Liu H, Zhou B, Liao Y, Wang Z
Received 19 December 2018
Accepted for publication 27 May 2019
Published 2 July 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 5153—5162
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S198802
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Gaetano Romano
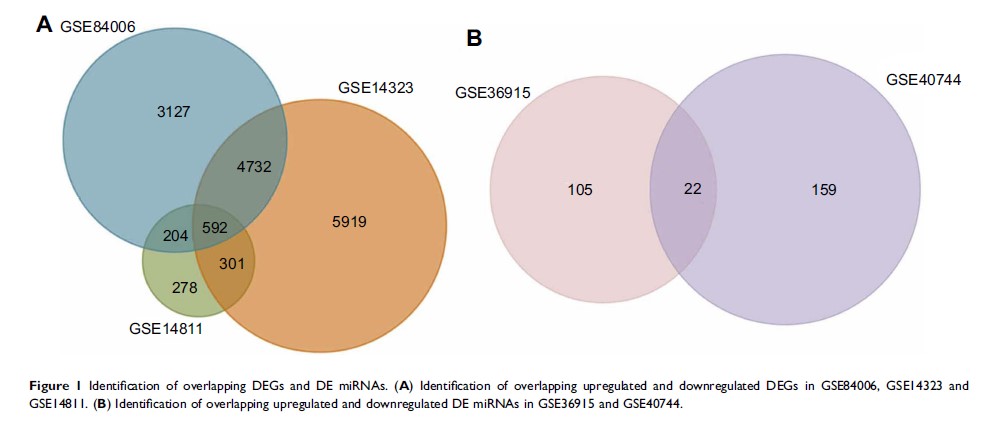
Background: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the second leading cause of death among cancers worldwide. In this study, we aimed to identify the molecular target genes and detect the key mechanisms of HCC. Three gene expression profiles (GSE84006, GSE14323, GSE14811) and two miRNA expression profiles (GSE40744, GSE36915) were analyzed to determine the molecular target genes, microRNAs (miRNAs) and the potential molecular mechanisms in HCC.
Methods: All profiles were extracted from the Gene Expression Omnibus database. The identification of the differentially expressed genes (DEGs) was analyzed by the GEO2R method. Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway and gene ontology (GO) enrichment analysis performed database for Integrated Discovery, Visualization and Annotation. The miRNA-gene network and protein–protein interaction (PPI) network were correlated by the Cytoscape software. The key target genes were identified by the CytoHubba plugin, Molecular Complex Detection (MCODE) plugin and miRNA-gene network. The identified hub genes were testified for survival curve using the Kaplan–Meier plotter database.
Results: Expression profiles had 592 overlapped DEGs. The majority of the DEGs were enriched in membrane-bounded organelles and intracellular membrane-bounded organelles. These DEGs were significantly enriched in metabolic, protein processing in the endoplasmic reticulum and thyroid cancer pathways. PPI network analysis showed these genes were mostly involved in the pathogenic Escherichia coli infection and the regulation of actin cytoskeleton pathways. Combining these results, we identified 10 key genes involving in the progression of HCC. Finally, PLK1 , PRCC , PRPF4 and PSMA7 exhibited higher expression levels in HCC patients with poor prognosis than those for lower expression via Kaplan–Meier plotter database.
Conclusion: PLK1 , PRCC , PRPF4 and PSMA7 could be potential biomarkers or therapeutic targets for HCC. Meanwhile, the metabolic pathway, protein processing in the endoplasmic reticulum and the thyroid cancer pathway may play vital roles in the progression of HCC.
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma, DEGs, bioinformatic analysis, KEGG pathway, PPI network, miRNA-gene network