111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

华南地区宫颈癌前病变和急性宫颈炎的血清生物标志物质谱鉴定与分析
Authors Qiu F, Su B, Li Z, Chen W, Cao L, Chen F, Liu D, He J, Lin N
Received 12 February 2019
Accepted for publication 29 May 2019
Published 4 July 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 6151—6162
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S205052
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Chien-Feng Li
Background: According to the statistics of WHO/IARC, cervical cancer (CC) has become the fourth malignant cancer of female worldwide and it is one of the main causes of death of women in developing countries.
Purpose: Potential plasma and metabolic biomarkers for CC precancerous lesions and cervicitis were indicated by LC-MS techniques, and their underlying mechanisms and functions were analyzed.
Methods: Plasma samples were selected from healthy people (control), low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions (LSIL), high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions (HSIL), CC, and post-treatment patients. All polypeptide types and sequences were detected by LC-MS/MS and the results were normalized by using Pareto-scaling. Potential metabolic biomarkers were screened by applying MetaboAnalyst 4.0 software and XCMS software, and analysis of variance and enrichment analysis were performed. Metabolic pathway analysis and functional enrichment analysis were used to further investigate the significance and pathological mechanisms of potential biomarkers.
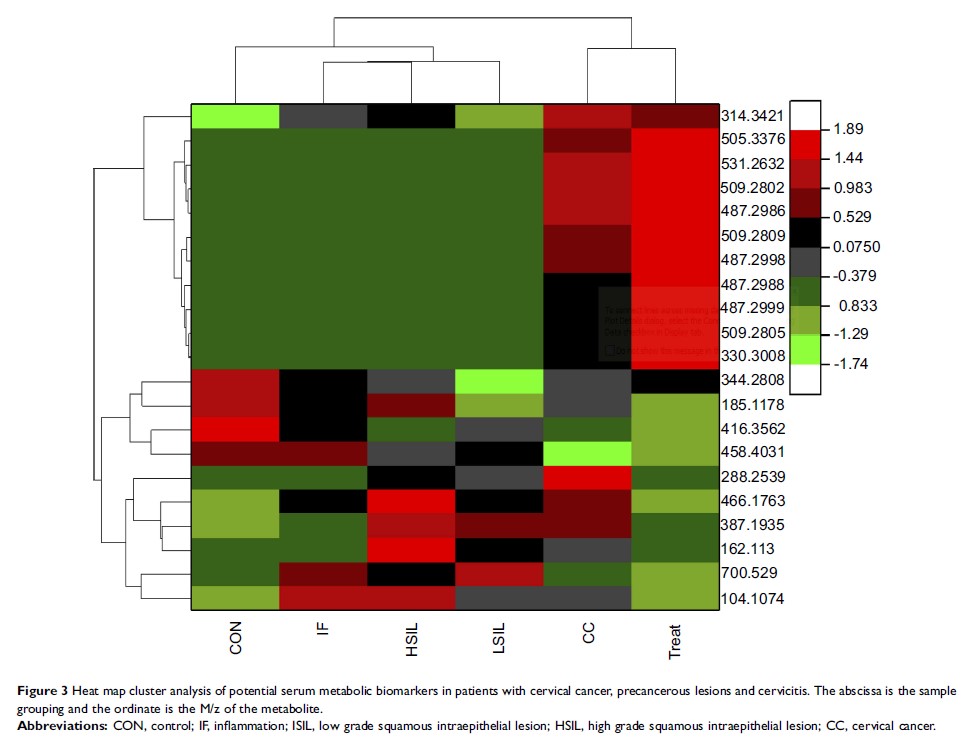
Results: Compared with healthy people, 9 differentially expressed metabolites were screened, 4 of which were up-regulated and 5 were down-regulated. LSIL group screened 7 differentially expressed metabolites, 5 of which were up-regulated and 2 were down-regulated; CC group screened 12 differentially expressed metabolites were screened, of which 9 were up-regulated and 3 were down-regulated. Eight differentially expressed metabolites were screened in the IF group, of which 5 showed up-regulation and 3 showed down-regulation. In functional enrichment analysis, differential metabolism was found to be associated with addition and coagulation cascades. Among all potential biomarkers, 2-amino-3-methyl-1-butanol, L-carnitine, Asn Asn Gln Arg, Ala Cys Ser Trp, Soladulcidine, Ala Ile Gln Arg, 2-amino-3 -Methyl-1-butanol, L-carnitine, Asn Asn Gln Arg, Ala Cys Ser Trp, Soladulcidine, Ala Ile Gln Arg can be used as predictors of precancerous lesions at different stages of CC. Among all biomarkers, 6α-fluoro-11β1,17-dihydroxypren-4-ene-3,20-dione has higher expression in the CC and HSIL groups and lower expression in the treatment group.
Conclusion: By applying molecular markers to assess the progression of the disease, the accuracy and specificity of the diagnosis can be improved, which has certain prospects in clinical applications.
Keywords: cervical precancerous lesion, acute cervicitis, LC-MS, metabonomics, serum biomarkers