111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

角膜溃疡患者的静息功能磁共振成像(fMRI)和功能连接密度图
Authors Zhu F, Tang L, Zhu P, Lin Q, Yuan Q, Shi W, Li B, Ye L, Min Y, Su T, Shao Y
Received 30 March 2019
Accepted for publication 10 June 2019
Published 5 July 2019 Volume 2019:15 Pages 1833—1844
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S210658
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Yu-Ping Ning
Purpose: To investigate alternations in spontaneous brain activities reflected by functional connectivity density (FCD) in patients with corneal ulcer (CU) using resting-state functional connectivity (rsFC).
Methods: We recruited 24 patients with CU (12 males, 12 females), and 24 healthy controls (HCs; 12 males, 12 females) matched for age, gender and education status. Functional magnetic resonance imaging examinations were performed on all subjects in a resting state and the following parameters determined: rsFC, long-range FCD (longFCD) and short-range FCD (IFCD). Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were then used to differentiate patients with CU from HCs.
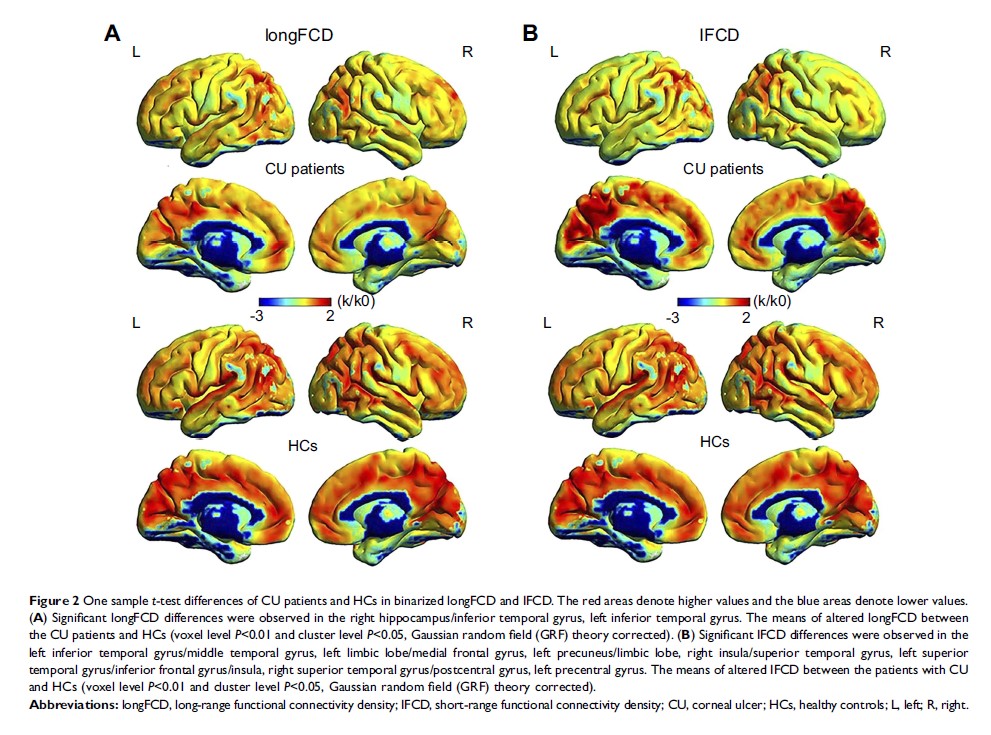
Results: Compared with HCs, CU patients showed significantly reduced rsFC values in the right cerebellum posterior lobe gyrus, right middle frontal gyrus/inferior frontal gyrus/superior frontal gyrus and left inferior parietal lobule/precuneus. Significantly reduced longFCD values were found in the right hippocampus/inferior temporal gyrus and the left inferior temporal gyrus. Moreover, compared with HCs, IFCD values were significantly reduced in the left inferior temporal gyrus/middle temporal gyrus, left limbic lobe/medial frontal gyrus, and left precuneus/limbic lobe, but were significantly increased in the right insula/superior temporal gyrus, left superior temporal gyrus/inferior frontal gyrus/insula, right superior temporal gyrus/postcentral gyrus, and left precentral gyrus.
Conclusions: Patients with CU exhibited alterations in spontaneous brain activities in several brain areas. These novel findings may help to reveal the neuropathological mechanisms underlying CU. This study provides a direction for further exploration of underlying neural mechanisms of CU and facilitate the clinical diagnosis and treatment of CU.
Keywords: functional connectivity density, corneal ulcer, spontaneous brain activities