111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

低成本提醒包的有效性与基于病例的健康教育相结合,可改善高血压患者的药物依从性:一项集群随机对照试验
Authors Shen Y, Wang T, Gao M, Zhu X, Zhang X, He C, Li Y, Sun X
Received 14 November 2018
Accepted for publication 30 May 2019
Published 10 July 2019 Volume 2019:13 Pages 1083—1092
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/PPA.S194667
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Naifeng Liu
Purpose: Medication adherence (MA) is a key factor for hypertensive patients’ blood pressure control and forgetfulness is one of the main reasons that cause medication non-adherence. If effective, low-cost reminder package (LCRP) has great potentials for large-scale promotion. Therefore, this study aims to evaluate the effectiveness of combining LCRP and health education to improve MA among hypertensive patients.
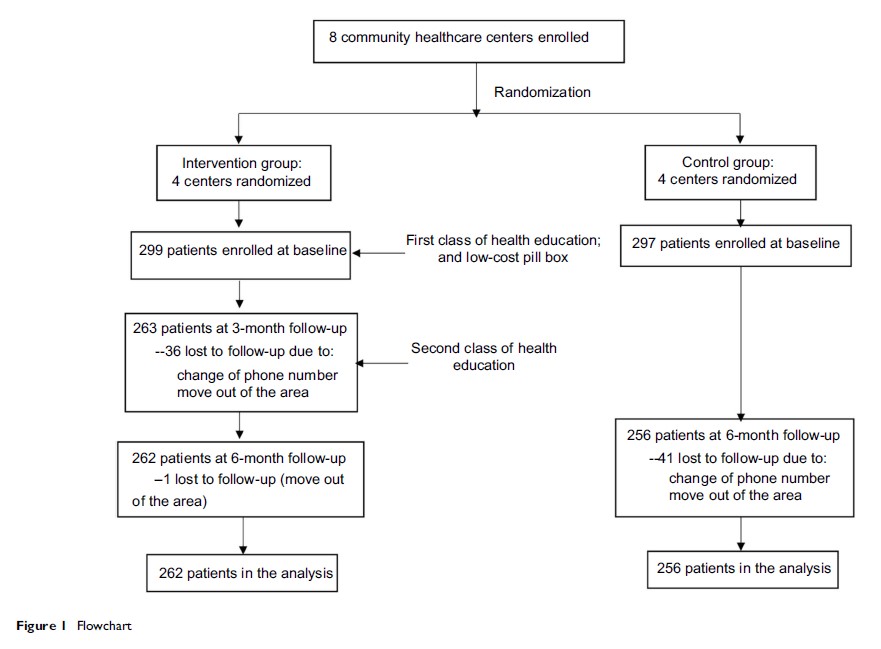
Patients and methods: A clustered randomized controlled trial was performed in Beijing. A total of 518 hypertensive patients recruited from 8 community health care centers were randomized to receive LCRP combined with case-based health education or usual care. Randomization was performed at community level. Multilevel modeling was used to evaluate the study effect.
Results: MA scores did not differ significantly at baseline between the intervention group and the control group. The results of multilevel modeling indicated that MA scores increased more in the intervention group, and the intervention effect on MA was 0.287 (95% CI: [0.103, 0.471], P =0.002). Patients’ systolic blood pressure (SBP) and diastolic blood pressure (DBP) were not improved (SBP: difference=0.536, 95% CI [−3.207, 4.278]; DBP: difference=−0.927, 95% CI [−3.283, 1.428]).
Conclusion: LCRP combined with case-based health education could significantly improve hypertensive patients’ MA.
Keywords: low-cost reminder package, medication adherence, multilevel modeling, case-based health education