111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

番茄红素通过抑制线粒体通透性转换孔开放来预防心肌缺血再灌注损伤
Authors Li X, Jia P, Huang Z, Liu S, Miao J, Guo Y, Wu N, Jia D
Received 15 November 2018
Accepted for publication 22 May 2019
Published 11 July 2019 Volume 2019:13 Pages 2331—2342
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S194753
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Andrew Yee
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sukesh Voruganti
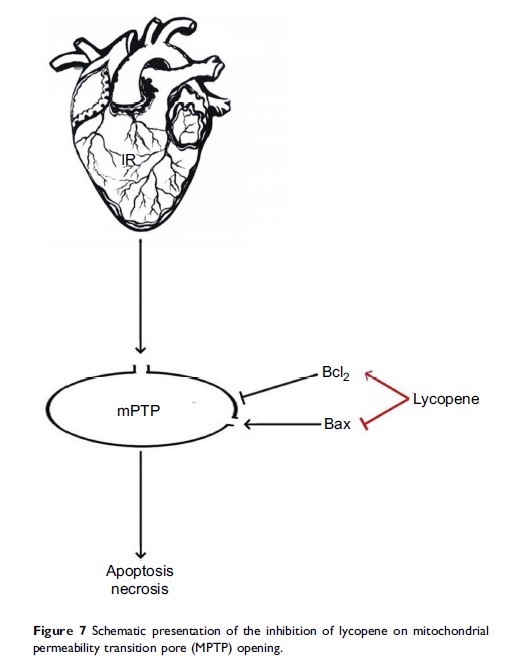
Background: Mitochondria permeability transition pore (MPTP) is an important therapeutic target for myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury (MIRI). Lycopene (LP) is a potent antioxidant extracted from the mature fruits of plants and has been reported to protect against MIRI; however, its mechanism of action has yet to be completely elucidated. The present study aimed to investigate the role of MPTP in the cardioprotection of LP.
Methods: H9c2 cells were pretreated with LP for 12 hrs and were subjected to 12-hr hypoxia/1-hr re-oxygenation, and cell viability was measured by a Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) assay. Male rats were subsequently intraperitoneally injected with LP for 5 consecutive days. At 24 hrs following the final injection, the rat hearts were isolated and subjected to 30-min ischemia/120-min reperfusion using Langendorff apparatus. The myocardial infarct size was measured by a TTC stain. Opening of the MPTP was induced by CaCl2 and measured by colorimetry. The change in mitochondrial transmembrane potential (ΔΨm) was observed under a fluorescence microscope. Apoptosis was measured by flow cytometry and a TUNEL stain, and the expression of apoptosis-related proteins was detected by Western blotting.
Results: LP pretreatment significantly increased cell viability, reduced myocardial infarct size and decreased the apoptosis rate. In addition, opening and the decrease of ΔΨm were attenuated by LP and the expressions of cytochrome c, APAF-1, cleaved caspase-9 and cleaved caspase-3 were also decreased by LP. However, these beneficial effects on MIRI were abrogated by the MPTP opener (atractyloside). Furthermore, LP treatment markedly increased Bcl-2 expression, decreased Bax expression and the Bax/Bcl-2 ratio.
Conclusion: The results of the present study demonstrated that LP protects against MIRI by inhibiting MPTP opening, partly through the modulation of Bax and Bcl-2.
Keywords: myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury, lycopene, mitochondrial permeability transition pore, apoptosis