111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

12-脂氧合酶通过胃癌细胞中的 Wnt/β-catenin 信号通路促进上皮 - 间质转化
Authors Yang XH, Zhuang MK, Xie WH, Du F, Huang YH, Chen ZX, Chen FL, Wang XZ
Received 13 January 2019
Accepted for publication 28 April 2019
Published 11 July 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 5551—5561
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S201373
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Shreya Arora
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Jianmin Xu
Background: 12-Lipoxygenase (12-LOX) plays a major role in the progression and metastasis of various types of cancer. In gastric cancer (GC), the expression level of 12-LOX is significantly up-regulated; however, its function, and underlying mechanism of action remain unclear.
Methods: The mRNA and protein expression levels of 12-LOX were assessed using quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) and Western blot analyses, respectively, in GC cell lines. 12-LOX expression was stably up-regulated using lentiviral vector in BGC823 and MGC803 cells, and cell-counting kit-8 (CCK8), colony formation, and invasion assays were performed to verify the function of 12-LOX in proliferation and metastasis. In addition, the expression levels of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) differentiation markers and downstream targets of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway were examined by Western blotting. A nude mouse model of tumor growth and metastasis was established to investigate the role of 12-LOX in vivo.
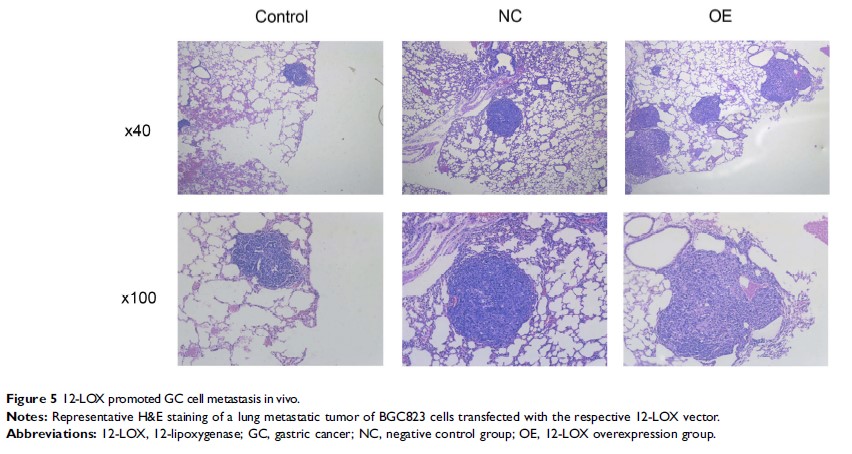
Results: Our findings demonstrate that 12-LOX mRNA and protein were highly expressed in GC cell lines. 12-LOX overexpression promoted GC cell proliferation, migration, and invasion both in vitro and in vivo. In addition, up-regulation of 12-LOX promoted the EMT in GC cells, as reflected by a decrease in E-cadherin expression and an increase in N-cadherin and Snail expression. 12-LOX overexpression in GC cells also increased the expression of multiple downstream targets of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.
Conclusion: These findings revealed that 12-LOX functions as an oncogene in promoting GC cell proliferation and metastasis in vitro and in vivo. In addition, 12-LOX might regulate the EMT via the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, indicating a potential role for 12-LOX as a target in GC treatment.
Keywords: 12-lipoxygenase, EMT, Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, gastric cancer