111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

苹果酸酶 1(ME1)是胃癌细胞中潜在的致癌基因,与胃癌患者的生存率低有关
Authors Shi Y, Zhou S, Wang P, Guo Y, Xie B, Ding S
Received 28 January 2019
Accepted for publication 17 June 2019
Published 11 July 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 5589—5599
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S203228
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Aruna Narula
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr William Cho
Background and objective: Gastric cancer is one of the most common cancers worldwide. However, the mechanisms associated with this disease are still not clear. Malic enzyme 1 (ME1) is a metabolic enzyme that is overexpressed in various cancers. Here, we examined whether it is involved in gastric cancer.
Methods: ME1 expression was knocked down in the gastric cancer cell line SGC7901. Cell growth and migration were measured using a real-time microelectronic cell sensor system. Cell invasion was measured using a Transwell assay. Cell cycle analysis was also performed to examine cell cycle arrest. A gastric cancer tissue microarray of gastric cancer was stained using immunohistochemistry. ME1 expression levels were also statistically analysed.
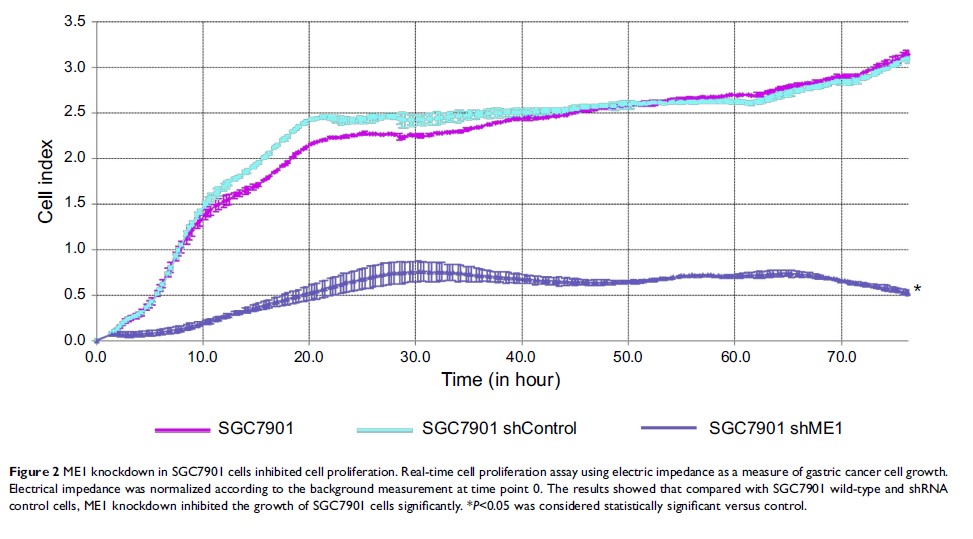
Results: ME1 knockdown in gastric cancer SGC7901 cells significantly inhibited cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. Cell cycle arrest was induced in the G2 phase. Further, ME1 expression was significantly correlated with gastric cancer patient prognosis based on both univariable and multivariable survival analysis. No significant difference was found between ME1 expression in gastric cancer tissues and that in adjacent tissues.
Conclusion: Our results provide evidence that ME1 is a key factor for gastric cancer. ME1 might be pro-oncogenic during both the development and migration of gastric cancer; it also might be related to gastric cancer patient survival.
Keywords: gastric cancer, malic enzyme 1, cell proliferation, migration, patients’ survival