111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

LncRNA LINC00668 通过抑制细胞凋亡和加速细胞周期来促进乳腺癌的进展
Authors Qiu X, Dong J, Zhao Z, Li J, Cai X
Received 27 September 2018
Accepted for publication 6 March 2019
Published 11 July 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 5615—5625
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S188933
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sanjeev Srivastava
Objective: To elucidate how lncRNA 00668 (LINC00668) influences the development of breast cancer (BC).
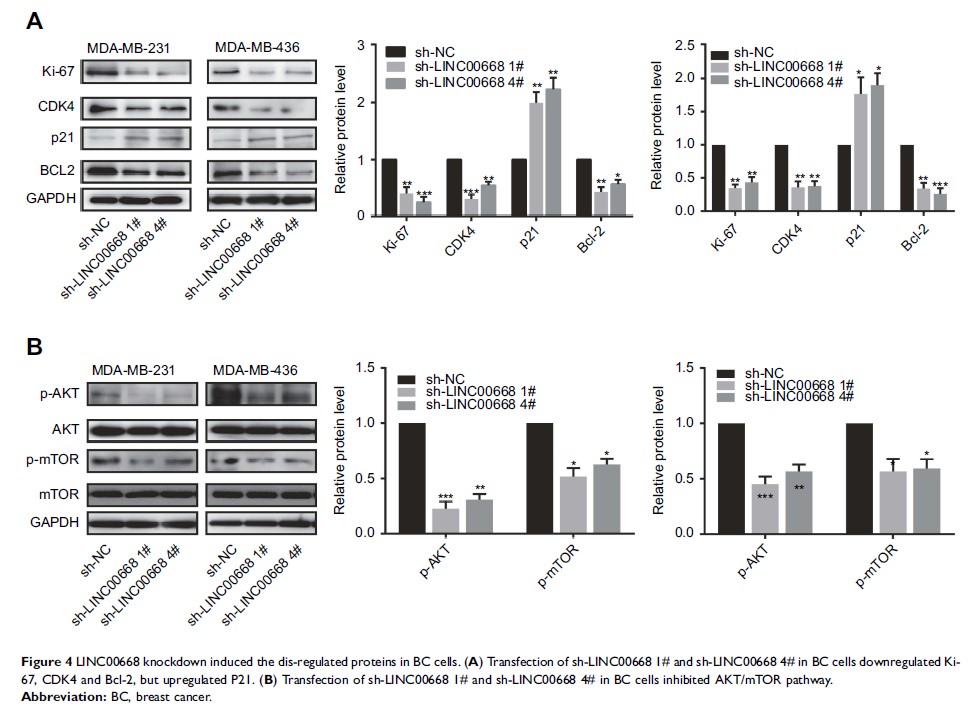
Materials and methods: Genome-wide expression profile of BC and paracancerous tissues were downloaded from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) and BC tissues and paracancerous tissues enrolled from our hospital for analyzing the expression level of LINC00668 and its correlation with prognosis. GSEA was conducted to analyze the potential functions of LINC00668. By transfection of sh-LINC00668 in BC cells, proliferation, apoptosis, cell cycle and colony formation of BC cells were accessed. Western blot was conducted to detect protein expressions of Ki-67, CDK4, Bcl-2, p21 and genes in AKT/mTOR pathways after LINC00668 knockdown in BC cells. Finally, tumor-bearing nude mice were administrated with BC cells. We compared the proliferative rate in mice with different administrations. Immunohistochemistry was carried out to access expression levels of Ki-67, CDK4, Bcl-2 and P21 in mice.
Results: Both TCGA data and BC tissues harvested from our hospital indicated the higher expression of LINC00668 in BC tissues. LINC00668 expression was negatively correlated to prognosis of BC patients. GSEA pointed out that LINC00668 is enriched in regulations of cell cycle and apoptosis. By transfection of sh-LINC00668 in MDA-MB-231 and MDA-MB-436 cells, the proliferative and colony formation abilities of BC cells decreased. Besides, LINC00668 knockdown in BC cells induced apoptosis and arrested cell cycle. LINC00668 knockdown downregulated Ki-67, CDK4 and Bcl-2, but upregulated p21. The AKT/mTOR pathway was inhibited after LINC00668 silenced. In vivo experiments demonstrated the decreased proliferative rate in tumor-bearing mice administrated with sh-LINC00668 transfected BC cells. Consistently, immunohistochemical results showed lower positive expressions of Ki-67, CDK4 and Bcl-2, but higher positive expression of p21 in sh-LINC00668 group.
Conclusion: LINC00668 is highly expressed in BC tissues and can promote the progression of BC by inhibiting apoptosis and accelerating cell cycle progression.
Keywords: LINC00668, breast cancer, apoptosis, cell cycle