111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

MicroRNA-218 通过靶向存活来调节宫颈癌细胞的化学敏感性
Authors Yu M, Xu B, Yang H, Xue S, Zhang R, Zhang H, Ying X, Dai Z
Received 27 December 2018
Accepted for publication 10 April 2019
Published 12 July 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 6511—6519
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S199659
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Antonella D'Anneo
Background: Cervical cancer is one of the most lethal malignancies among women in the world. Every year about 311,365 women die because of cervical cancer. Chemo-resistance is the main reason of the lethal malignancies, and the mechanism of chemo-resistance in cervical cancer still remains largely elusive.
Purpose: Previous studies reported that microRNAs played important biological roles in the chemo-resistance in many types of cancers, in the present study we tried to investigate the biological roles of microRNA-218 in chemo-resistance in cervical cancer cells.
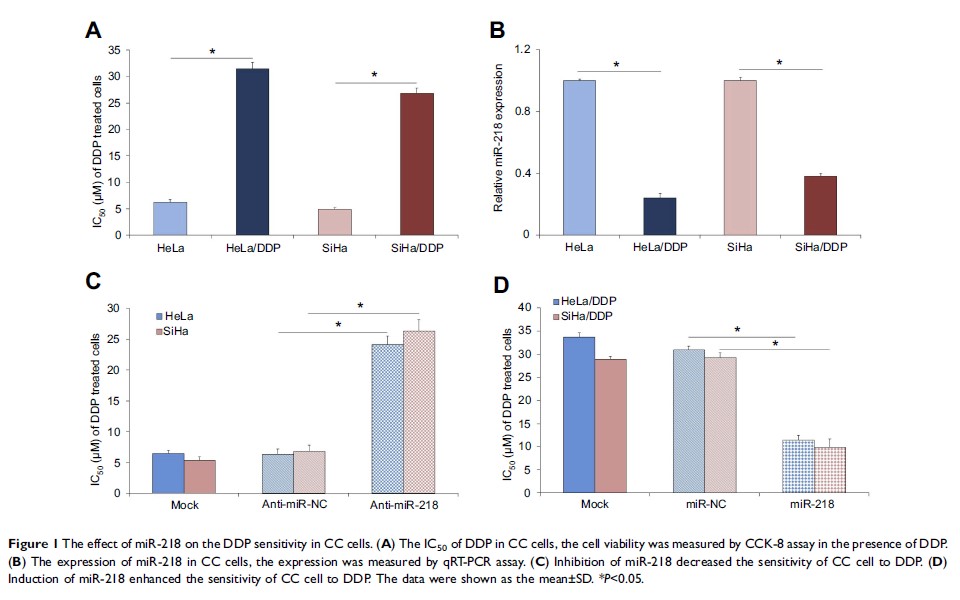
Results: Real-time PCR results indicated microRNA-218 was downregulated in cisplatin-resistant HeLa/DDP and SiHa/DDP cells compared with the mock HeLa and SiHa cells. CCK-8 assay results showed upregulation of microRNA-218 enhanced the cisplatin sensitivity of cervical cancer cells; while downregulation of microRNA-218 decreased the cisplatin sensitivity of cervical cancer cells. Dual-luciferase assay indicated survivin was a direct target of microRNA-218. Western blotting and PCR results indicated the expression of survivin in HeLa/DDP and SiHa/DDP cells was significantly increased compared with HeLa and SiHa cells. Further study indicated induction of microRNA-218 decreased the expression of survivin while inhibition of microRNA-218 increased the expression of survivin in cervical cancer cells. Cell apoptosis results indicated induction of microRNA-218 induced the cell apoptosis in cervical cancer cells.
Conclusion: Our data revealed microRNA-218 enhanced the cisplatin sensitivity in cervical cancer cells through regulation of cell growth and cell apoptosis, which could potentially benefit to the cervical cancer treatment in the future.
Keywords: miR-218, cervical cancer, cisplatin resistant, apoptosis, surviving